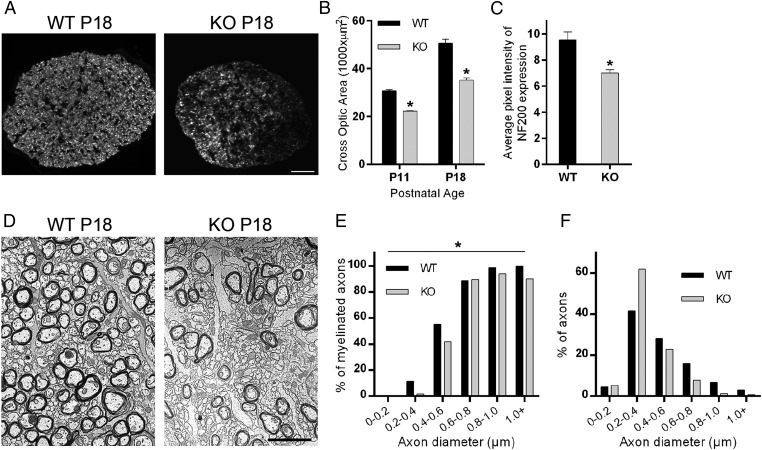
Fig. 4.
Contactin regulates optic nerve thickness and myelin development. (A) Contactin WT and KO optic nerve cross sections were stained for NF200 at P18. (Scale bar, 30 µm.) (B) Contactin deficiency resulted in reduced optic nerve thickness compared with WT at P11 (*P < 0.01, n = 4) and P18 (*P < 0.01, n = 4). (C) Cntn1-KO nerves had reduced NF200 expression compared with WT at the same age (*P = 0.01, n = 4). (D) Electron micrographs show 60% reduction in numbers of myelinated axons and increased numbers of small-diameter axons in KO samples compared with WT at P16 (see text for details). (Scale bar, 2.5 µm.) (E) The graph shows percentage of myelinated axons according to axon diameter for KO and WT mice. In the KO condition, reduced myelination was most evident for axons with diameters less than 0.6 µm. (F) Analyses of axon diameters revealed an increased ratio of small-diameter axons (0.2–0.4 µm) and reduced ratios for larger-diameter axons for KO. Quantification for E and F was performed with more than 1,000 axons per genotype. The overall difference between WT and KO by two-way ANOVA was significant for E (*P < 0.05) but not significant for F (P > 0.05).