Fig. 4.
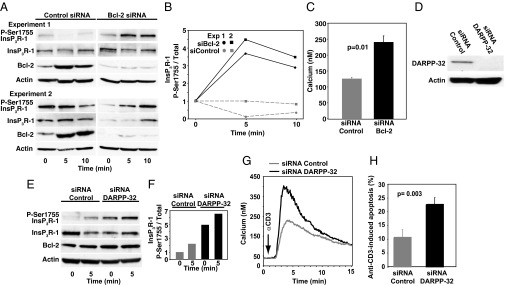
Knockdown of Bcl-2 or DARPP-32 reverses Bcl-2’s inhibition of InsP3R-1 phosphorylation, Ca2+ elevation, and apoptosis. (A) Immunoblots from two experiments in which siRNA Bcl-2 knockdown reversed Bcl-2’s inhibition of anti-CD3-induced P-Ser1755 InsP3R-1 elevation. (B) P-Ser1755 InsP3R-1 levels relative to total InsP3R-1 levels at 5 and 10 min after anti-CD3 addition; ratios representing the 0-min point (before anti-CD3) were normalized to a value of one (two experiments). (C) Symbols represent peak Ca2+ elevation (mean ± SEM, n = 3 experiments, 85 cells per treatment per experiment) induced by anti-CD3 in Jurkat cells and measured by digital imaging. Cells were pretreated with control siRNA or Bcl-2 siRNA to knockdown Bcl-2. (D) Immunoblot documenting DARPP-32 knockdown. (E) Immunoblot representative of two experiments with the same result, showing the effect of DARPP-32 knockdown on P-Ser1755 InsP3R levels before and 5 min after adding anti-CD3 to Jurkat cells. (F) P-Ser1755 InsP3R-1 levels relative to total InsP3R-1 levels 5 min after anti-CD3 addition (same experiments as in E; ratios representing the 0-min point before anti-CD3 addition were normalized to one). (G) Ca2+ elevation induced by anti-CD3 addition (arrow) in Jurkat cells pretreated with control or DARPP-32 siRNA. Traces represent average Ca2+ levels in 85 cells in a single experiment representative of three experiments. (H) Percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis 8–18 h after anti-CD3 addition (background apoptosis, before anti-CD3 addition, subtracted; mean ± SEM, six experiments).
