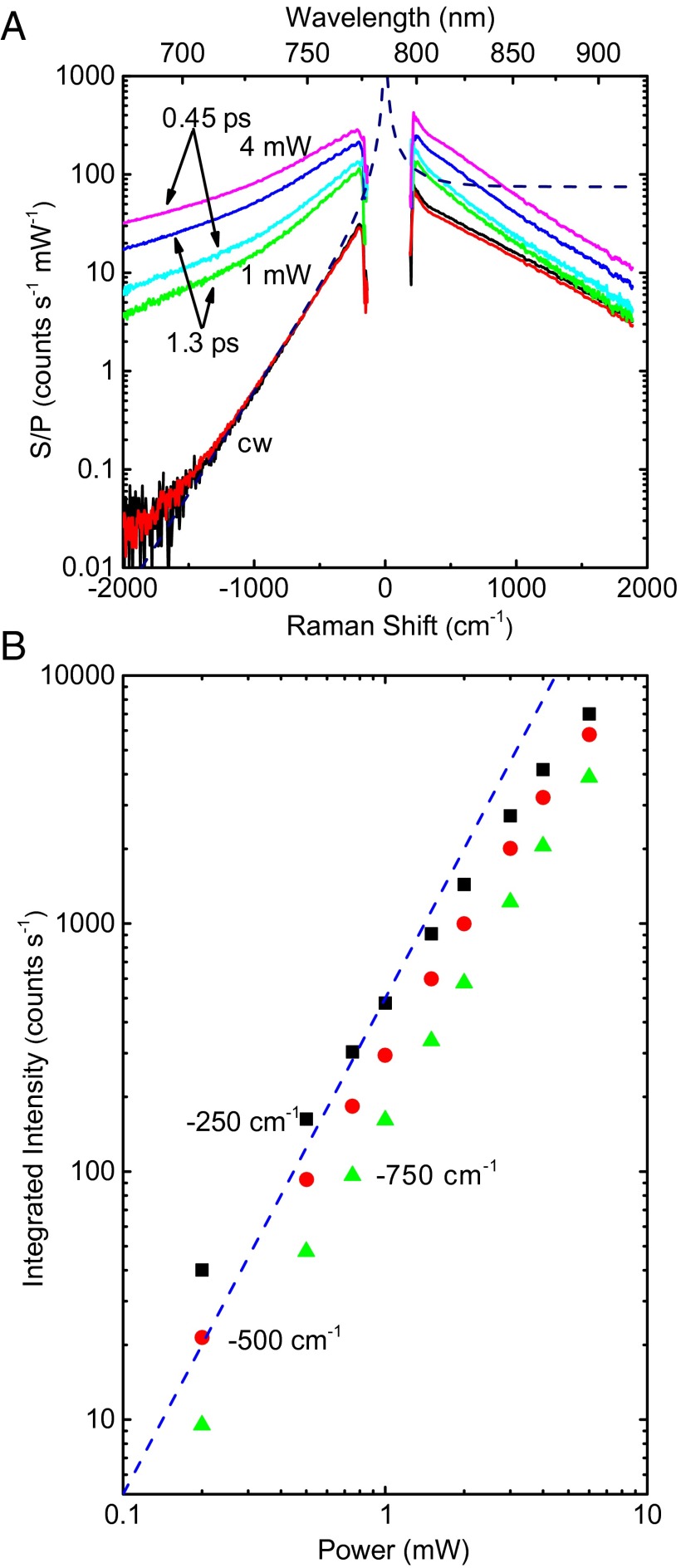
Fig. 2.
(A) Raman scattering spectra for AuNRs with the absorption peak at 787 nm excited by cw laser light at 785 nm at incident powers of 1 mW (black), 4 mW (red); by mode-locked laser pulses of 0.45-ps width with average incident powers of 1 mW (cyan) and 4 mW (magenta); and by mode-locked laser pulses of 1.3-ps width with average incident powers of 1 mW (green) and 4 mW (blue). The y axis is the same as in Fig. 1B: S is the scattered intensity, and P is the average power of the excitation laser. Data for 1 and 4 mW using the cw laser overlap. The dashed line is the calculated intensity for a characteristic temperature of 300 K assuming constant Raman cross-section and enhancement factors at all Raman shifts; the vertical scale of the dashed line is adjusted to match the experimental anti-Stokes intensity. (B) Raman scattering intensity vs. average incident power for AuNRs with absorption peak at 787 nm excited by pulsed 785-nm laser pulses of 0.45-ps width integrated over a Raman shift range of −240 to −260 cm−1 (black squares), −490 to −510 cm−1 (red circles), and −740 to −760 cm−1 (green triangles). The blue dashed line with a slope of 2 indicates a quadratic relation between the spectral intensity and average incident power.