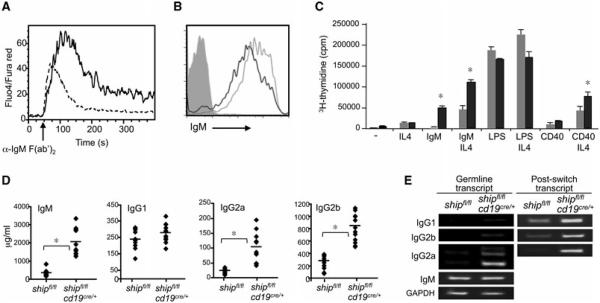
Figure 2.
B-cell conditional deletion of SHIP results in B cells hyperresponsive to BCR and IFN-γ stimulation. (A) Purified B cells from shipfl/flcd19cre/+ (solid line) and shipfl/fl (dashed line) mice (n = 3) were loaded with 5 μg/mL Fluo-4 and FuraRed. Activation of calcium flux was induced by 10 μg/mL of anti-IgM F(ab′)2 and the resulting changes were monitored by flow cytometry. Result shown are representative from one experiment out of three performed. (B) IgM surface expression detected by flow cytometry. Solid line: shipfl/flcd19cre/+; dashed line: shipfl/f; gray histogram: isotype control. Data shown are representative of three independent analyses performed (n = 3). (C) Proliferation assay of purified B cells (n = 3) (CD43-negative fraction of spleen) 3 days after activation with the indicated stimulus. Tritiated thymidine was added for the last 6 h. Gray bar: shipfl/fl; black bar: shipfl/flcd19cre/+. (D) Total serum immunoglobulin concentration of indicated isotypes was detected by ELISA in shipfl/fl and shipfl/flcd19cre/+ mice (n = 10). (E) Germline and postswitch transcripts that appeared during isotype switching were detected by RT-PCR. Results shown are representative of one out of three independent experiments. *p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test).