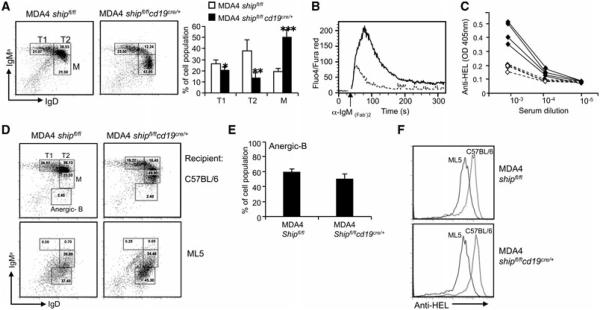
Figure 4.
Deletion of SHIP does not influence the establishment of B-cell tolerance to soluble HEL Ag. (A) FACS histogram and bar graph analysis of splenocyte populations: T1 (B220+, IgDlow, IgMahigh), T2 (B220+, I gDhigh, IgMahigh), and mature (B220+, IgDhigh, IgMalow) B cells. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.0005, ***p < 0.00001 (Student’s t-test). (B) Calcium release assay of MDA4 shipfl/flcd19cre/+ (solid line) and MDA4 shipfl/fl (dashed line), performed as in Figure 2A. (C) Anti-HEL Ab levels in serum from MDA4 shipfl/flcd19cre/+ (solid line) and MDA4 shipfl/fl (dashed line) mice were analyzed by ELISA. (D and E) BM cells were isolated from MDA4 shipfl/flcd19cre/+ or MDA4 shipfl/fl mice. A total of 1 × 107 cells were then transferred to lethally irradiated (960 rads) C57BL/6 (top) or ML5 (bottom) mice. Total spleen cells were collected after 2 months and the development of anergic B cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. (F) Surface anti-HEL expression on B cells isolated from the mice in (D) was analyzed by flow cytometry. (A and E) Data shown as mean + SD and (A–F) are representative of four independent experiments, n = 3 mice/group.