Figure 3. Perception of the knee-jerk reflex in the kick forward condition in a representative volunteer.
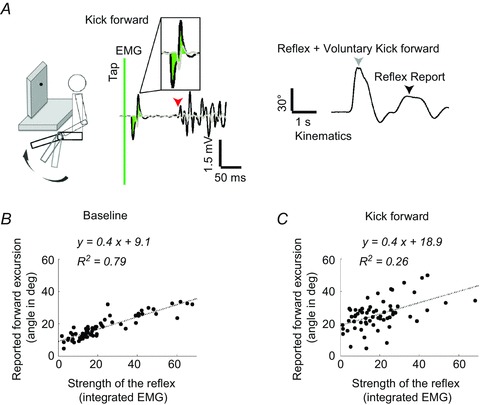
A, schematic view of the experimental set-up. Volunteers were instructed to kick forwards as soon as they felt the tendon tap. On the EMG traces, the time of tap is the green vertical bar. Note the strong reflexive and voluntary activation in quadriceps (black trace, arrow marks the voluntary EMG activity onset). The area used for analysis is shaded on the EMG trace. The grey arrow marks the end of the forward movement that consisted of both reflexive and voluntary contractions. The black arrow on the kinematic trace shows the position from which the volunteer perceived him/herself kicking forwards. B and C, strength of the reflexive contractions and the perceptual reports correlated well in the baseline condition (B) and poorly when kicking forwards (C).
