Figure 2.
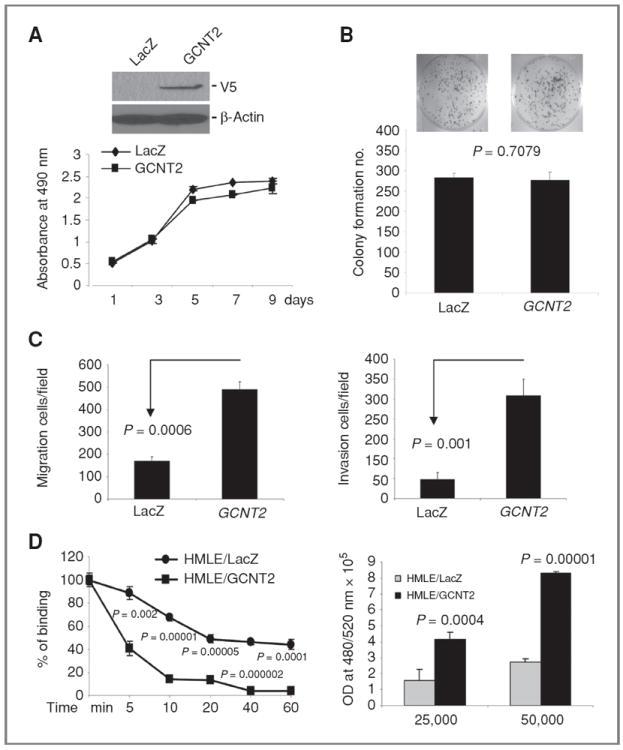
The effect of GCNT2 on cell proliferation, colony formation, cell migration, invasion, cell detachment, and attachment. A, ectopic expression of GCNT2 in HMLE cells detected by Western blotting (top). The effect of ectopic expression of GCNT2 on cell proliferation (low). B, the effect of ectopic expression of GCNT2 on colony formation in HMLE cells. C, the effect of ectopic expression of GCNT2 on cell migration (left) and invasion (right) in HMLE cells. D, the effect of GCNT2 on cell detachment and attachment. The left panel shows that ectopic expression of GCNT2 led to an increase in detachment of HMLE cells from plates when treated with EDTA (0.02%) at different times. The right panel shows that ectopic expression of GCNT2 led to an increase of cell adhesion to HUVEC cells. 25,000 and 50,000 HMLE-derived cells were plated on top of the monolayer of HUVEC cells.
