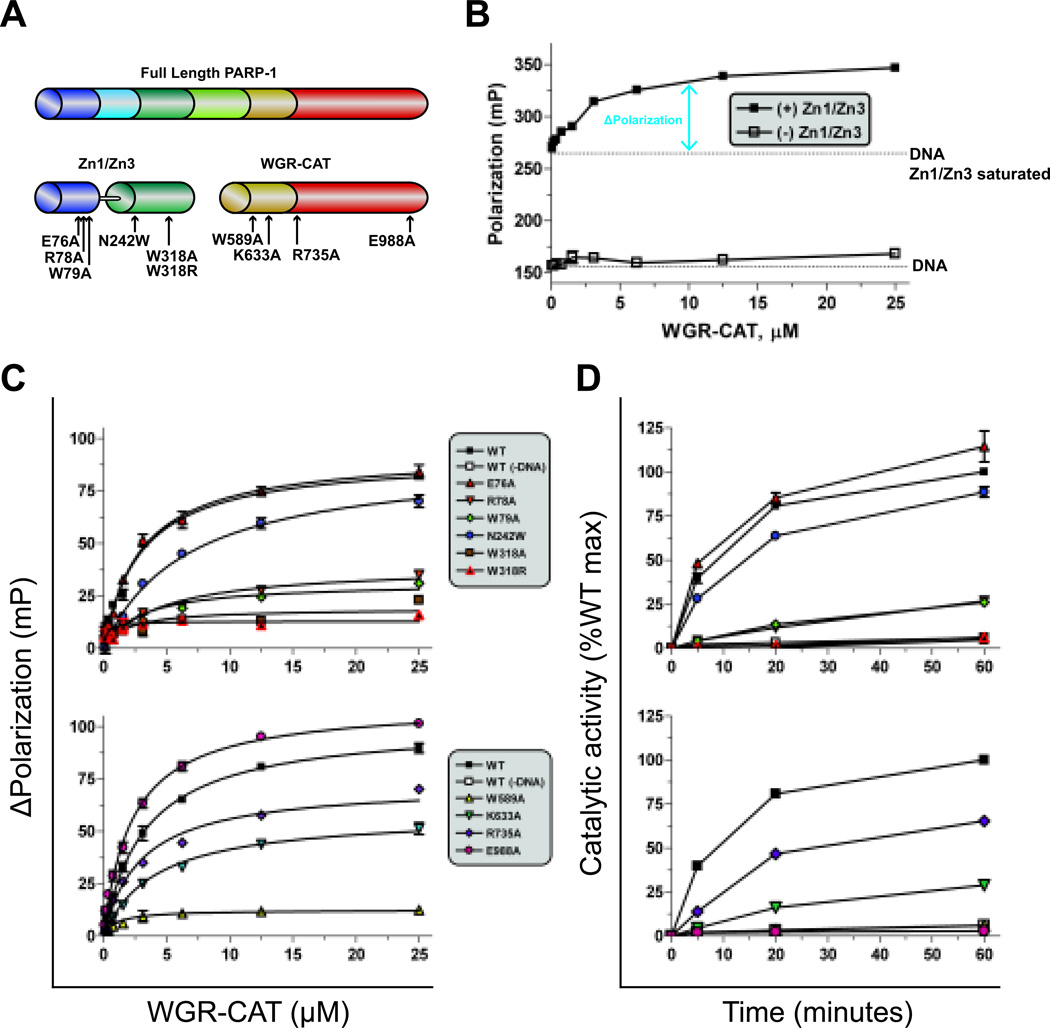
Figure 4.
A high-throughput (HT) fluorescent polarization (FP) assay to detect allosteric PARP-1 inhibitors. (A) Schematic of PARP-1 proteins used in this assay (Zn1-Zn3 and WGR-CAT), mapped with mutation sites. (B) Dose response of WGR-CAT binding to fluorescein-labeled DNA alone or to fluorescein-labeled DNA saturated with Zn1-Zn3. (C) WGR-CAT binding in the FP assay in the presence of Zn1-Zn3 (top) or WGR-CAT (bottom) mutations. (D) Catalytic activity of Zn1-Zn3 and WGR-CAT combinations using the colorimetric assay with mutations made in Zn1-Zn3 (top) or WGR-CAT (bottom).