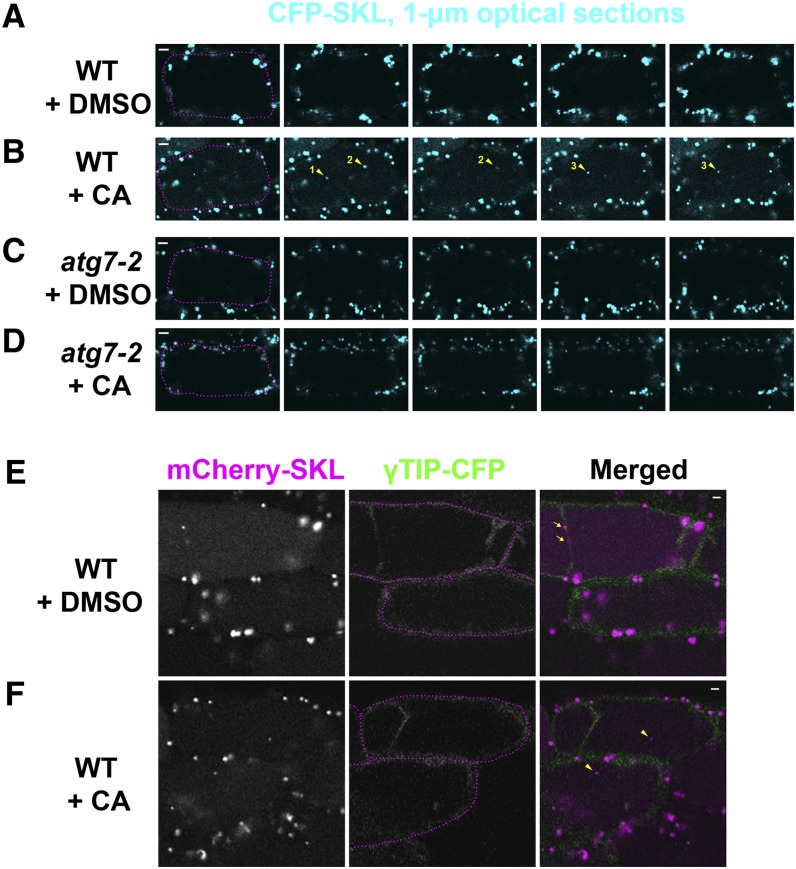
Figure 3.
Peroxisomal Protein Markers Are Degraded in the Vacuole of Wild-Type Hypocotyl Cells, but Not in the Vacuole of Autophagy-Defective Mutant Cells.
Seedlings were grown in liquid MS medium for 6 days and treated with either DMSO (A), (C), and (E) or 1 μM CA (B, D, and F) for 17 h before image acquisition. (A) to (D) Confocal Z-series of wild-type (A) and (B) or atg7-2 (C) and (D) transgenic hypocotyls expressing the Pro35S-CFP-SKL transgene. Optical sections were acquired at 1-μm intervals. Yellow arrowheads with numbers indicate three vacuolar CFP-SKL puncta stabilized by CA. Magenta dotted lines were added to images in the first column to highlight the boundary of each cell. (E) and (F) Confocal images of wild-type transgenic hypocotyls expressing both the Pro35S-mCherry-SKL and Pro35S-γ-TIP-CFP transgenes. Transvacuolar strands can be seen in the top cells at γ-TIP-CFP images. Magenta dotted lines were added to images in the middle column. In the merged images on the right, the signals of mCherry-SKL and γTIP-CFP are pseudocolored magenta and green, respectively. Two yellow arrows (E) label cytoplasmic peroxisomes in the transvacuolar strand. Two yellow arrowheads (F) indicate vacuolar mCherry-SKL bodies lacking γTIP-CFP signal. Representative images were chosen from at least four biological replicates. Bars =5 μm (A) to (D) or 2 μm (E) and (F).