Figure 1.
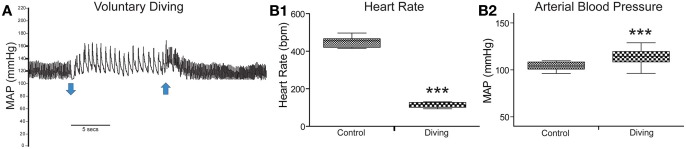
Cardiovascular responses to underwater submersion of voluntarily diving rats. The abrupt bradycardia and increase in mean arterial pressure (MAP) is seen in (A) upon submergence (down arrow), which immediately reverts to normal rhythms after emergence from the water (up arrow). Compilation of trials (n = 24) from eight rats showing the 80% drop in heart rate (B1; HR, p < 0.001) and increase in MAP (B2, p < 0.001) after underwater submersion. Rats exhibit an almost invariant diving response. ***p < 0.001.
