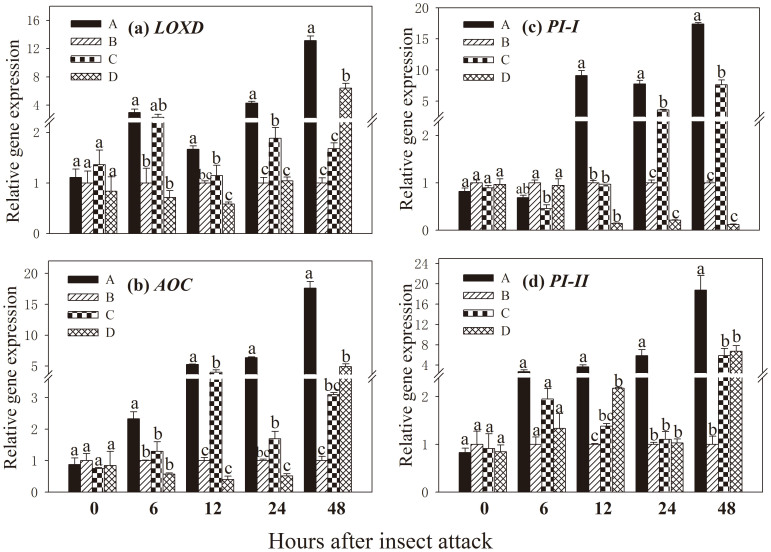
Figure 2. Expression of four defence-related genes in leaves of ‘receiver' tomato plants in response to common mycorrhizal networks (CMNs) connected with Spodoptera litura-infested neighbouring tomatoes.
Funneliformis mosseae was used to establish CMNs between ‘donor' and ‘receiver' tomatoes. Third instar larvae of Spodoptera litura were used to attack tomatoes. Quantitative real time RT-PCR was used to detect the transcripts of five defence-related genes encoding (a) lipoxygenase D (LOXD), (b) allene oxide cyclase (AOC), (c) proteinase inhibitor I (PI-I) and (d) proteinase inhibitor II (PI-II). Four treatments (A, B, C, D) were set up as described in Table 1. Values are means + standard error from three sets of independent experiments with three pots per treatment for each set of experiments. For each time point, letters above bars indicate significant difference among treatments (P < 0.05 according to Tukey's multiple range test). Results of ANOVA analysis are presented in the Supporting Information (Table S4).