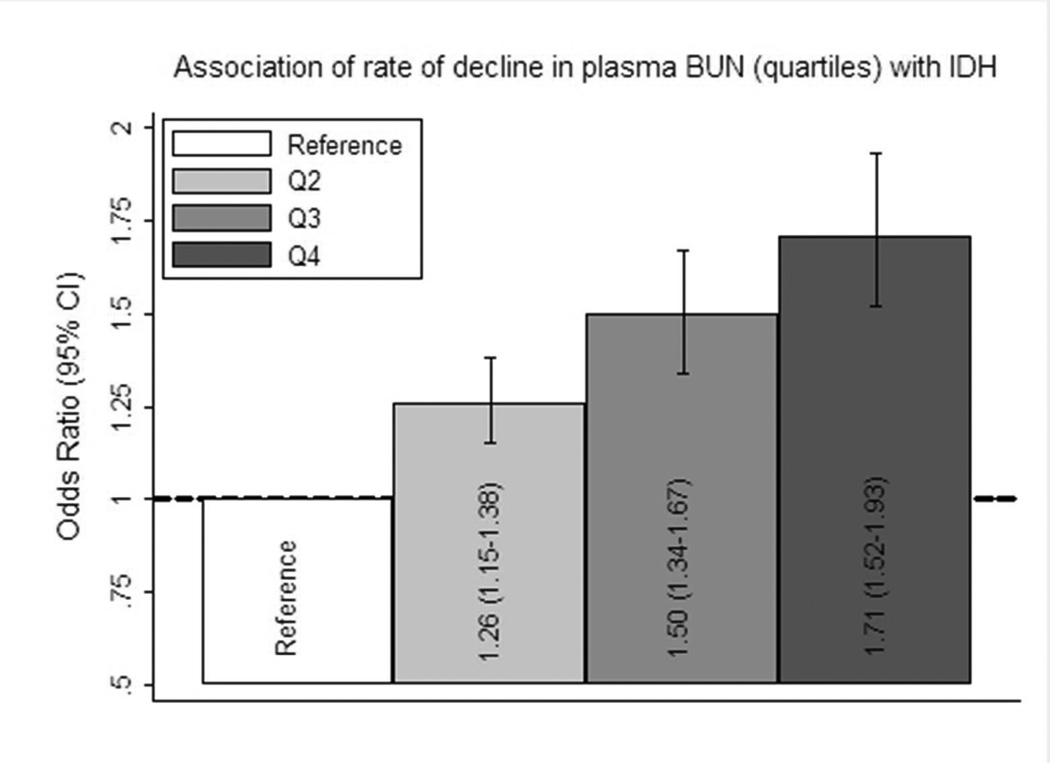
Figure 1. The association between quartiles of rate of decline in plasma BUN and intra-dialytic hypotension.
Associations between quartiles (Q; referent Q1) of rate of decline in plasma BUN and intra-dialytic hypotension (IDH) are presented as odds ratios (95% confidence intervals). Estimates were calculated using generalized linear models and adjusted for HEMO study flux assignment (higher vs lower), session length (≤180, >180, ≥210, ≥240 mins), blood flow (≤250, 250–349, 350–449, ≥450 mL/min), dialysate flow (0–500, 501–800, >800 mL/min), age, race (black, non-black), sex, post-dialysis weight, sex-by-weight cross-product terms, access, pre-dialysis SBP, height, ischemic heart disease, congestive heart failure (none, mild, moderate/severe), peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, arrhythmia, serum sodium, creatinine, albumin, phosphorus, bicarbonate and ultrafiltration requirement.