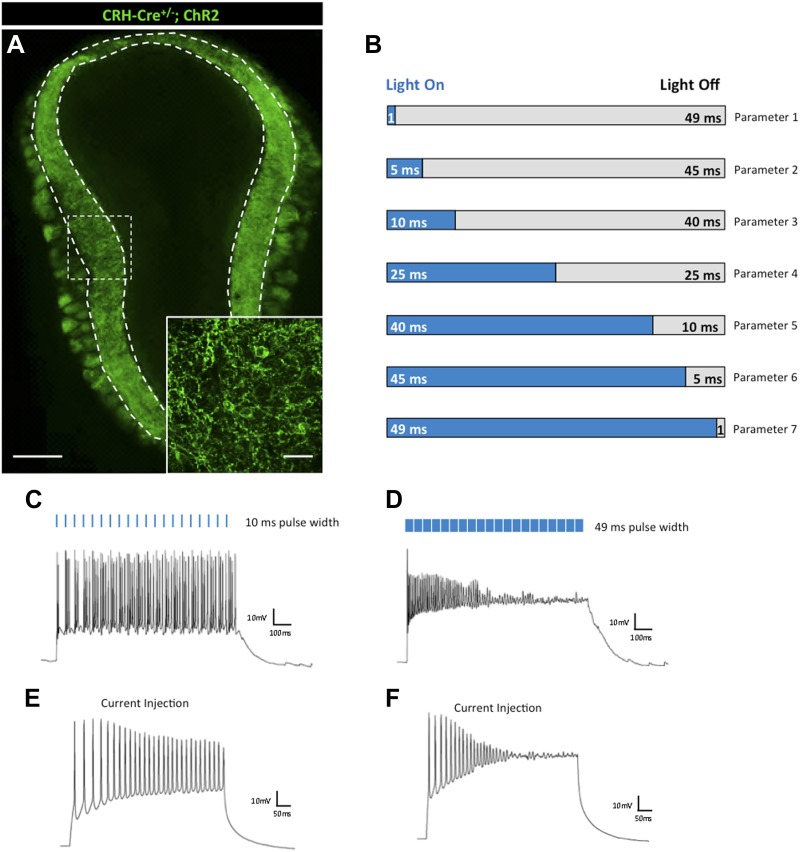
Figure 1. Effects of light pulse duration on CRH-expressing interneurons of the olfactory bulb.
(A) Crh-Cre+/−; ROSALSL-ChR2-EYFP mice express the ChR2-EYFP fusion protein in CRH-expressing interneurons of the external plexiform layer (EPL) of the main olfactory bulb (scale bar, 0.5 mm). Inlay represents zoomed image of ChR2-expressing interneurons of the EPL (scale bar, 100 μM). (B) Firing responses of ChR2-expressing neurons were recorded for seven different stimulation parameters. Each light stimulation parameter consists of a single train comprised of 20 light pulses (≈40 mW/mm2) at 20 Hz. Pulse width is the only condition that varies among the seven parameters. Parameter 1–1 ms pulse width/49 ms intervals, Parameter 2–5 ms pulse width/45 ms intervals, Parameter 3–10 ms pulse width/40 ms intervals, Parameter 4–25 ms pulse width/25 ms intervals, Parameter 5–40 ms pulse width/10 ms intervals, Parameter 6–45 ms pulse width/5 ms intervals, Parameter 7–49 ms pulse width/1 ms intervals. (C) Robust firing of a CRH-expressing EPL interneuron in response to brief light pulses (20 Hz, 10 ms pulse width). (D) Prolonged light pulse duration (20 Hz, 49 ms pulse width) leads to depolarization block in CRH interneurons. (E) Moderate current injection (60 pA) elicits regular firing of ChR2-expressing CRH interneurons. (F) High current injection (160 pA) results in depolarization block of ChR2-expressing CRH interneurons.