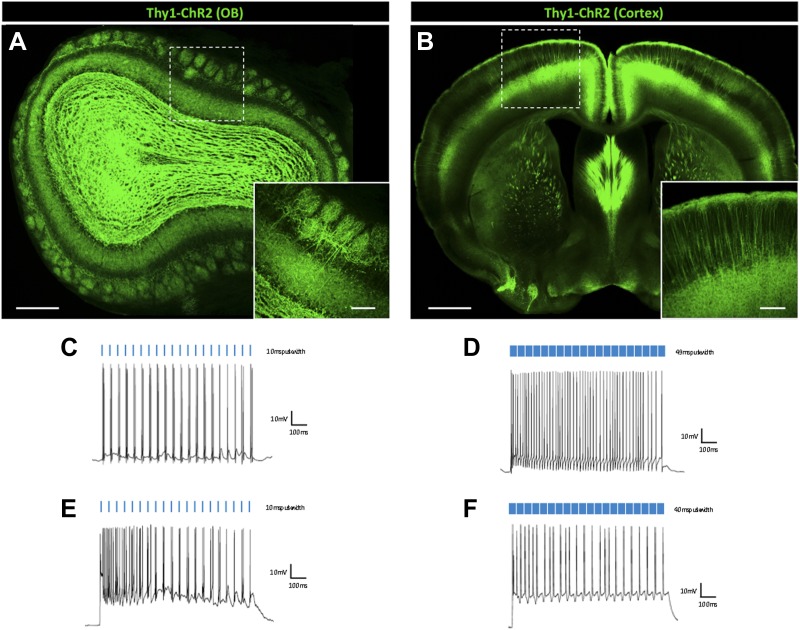
Figure 5. Principal excitatory cell types are less susceptible to light-induced depolarization block.
Thy1-ChR2 transgenic mice display ChR2-EYFP expression in (A) excitatory mitral cells of the main olfactory bulb (scale bar, 0.5 mm)—note that ChR2 expression is also observed throughout the granule cell layer of the olfactory bulb due to axon collaterals from mitral/tufted cells and ChR2-expressing centrifugal inputs from the piriform cortex–and (B) layer V cortical pyramidal neurons (scale bar, 1 mm). Inlays display zoomed images of ChR2-expressing olfactory bulb mitral cells (scale bar, 100 μM) or cortical pyramidal neurons (scale bar, 200 μM). (C) Mitral cells display steady firing in response to brief light pulses (20 Hz, 10 ms pulse width) and (D) enhanced firing in response to prolonged light pulse duration (20 Hz, 49 ms pulse width). (E) Steady firing of ChR2-expressing pyramidal cells in response to brief light pulse stimulation (20 Hz, 10 ms pulse width) and (F) prolonged light pulse duration (20 Hz, 40 ms pulse width). OB = Olfactory Bulb.