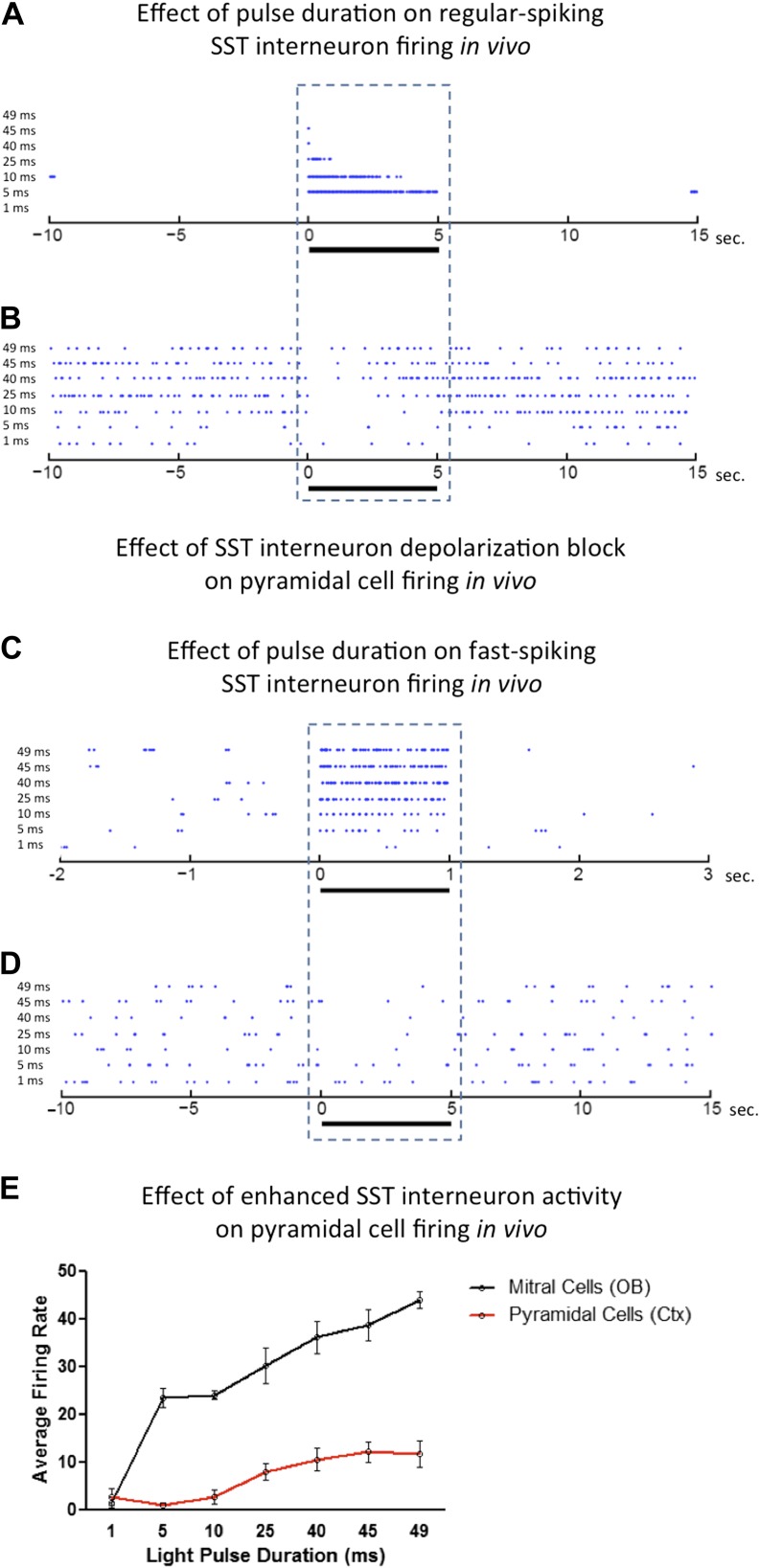
Figure 7. Effects of light pulse duration on ChR2-expressing neurons in vivo.
Increasing light pulse duration onto (A) a presumptive regular-spiking SST cortical interneuron (median latency to spike = 1.8 ms, N = 7 cells from 5 animals) leads to depolarization block and (B) disinhibition of a presumptive cortical pyramidal cell. Increasing light pulse duration onto (C) a presumptive fast-spiking SST cortical interneuron (median latency to spike = 6 ms, N = 3 cells from 5 animals) results in enhanced interneuron firing and (D) subsequent inhibition of a presumptive cortical pyramidal cell. In contrast to regular-spiking interneurons, increasing light pulse duration onto excitatory (E) mitral cells and cortical pyramidal cells enhance average firing rate with increasing pulse width. OB = Olfactory Bulb.