Figure 6.
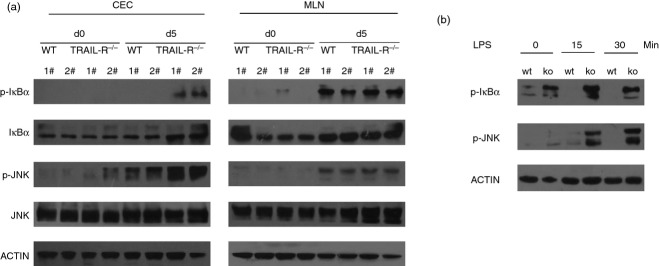
(a) The nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and Janus kinase (JNK) pathways are highly activated in tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor deficient (TRAIL-R−/−) colon epithelial cells (CEC) but not in mesenteric lymph node (MLN) cells. Protein lysates were prepared from CEC or MLN cells from WT or TRAIL-R−/− mice on day 0 or day 5 after dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) administration. Western blotting was performed with antibodies against IκBα, phospho-IκBα, JNK, phospho-JNK and actin. Each bar represents cell lysates from two individual mice. (b) CEC from TRAIL-R−/− mice were hyper-responsive to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. CEC from WT or TRAIL-R−/− mice were untreated or stimulated with LPS (20 μg/ml) for 15 or 30 min. Then, the cells were lysed, and the cell lysates were subjected to SDS–PAGE. Immunoblotting was performed to detect Toll-like receptor signalling components using anti-phospho-IκBα and anti-phospho-JNK antibodies.
