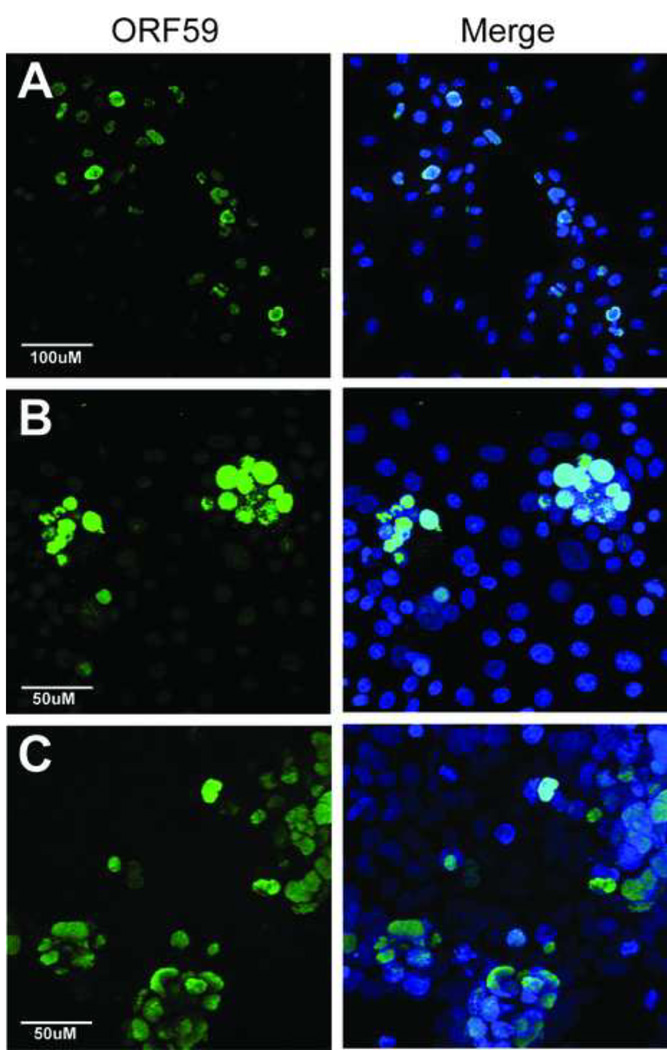
Figure 1. RRV infection induces lytic gene expression in a variety of cell lines from human and nonhuman Old World primate species.
(A) Rhesus primary fetal fibroblast (RPFF), (B) African green monkey kidney epithelial (Vero), and (C) human embryonic kidney epithelial (HEK293) cells were infected with RRV and evaluated three days post-infection for expression of the early lytic gene marker, the ORF59 DNA polymerase processivity factor, using rabbit anti-RV2 ORF59 antiserum (green), as described in Materials and Methods. The merged image of the ORF59 and Topro-3 (blue) nuclear staining is shown. Images were acquired by confocal microscopy and are shown as projections of the z-stack. The magnification scales are shown. Abundant RRV-infected ORF59-positive cell foci were detected in all three cell lines.