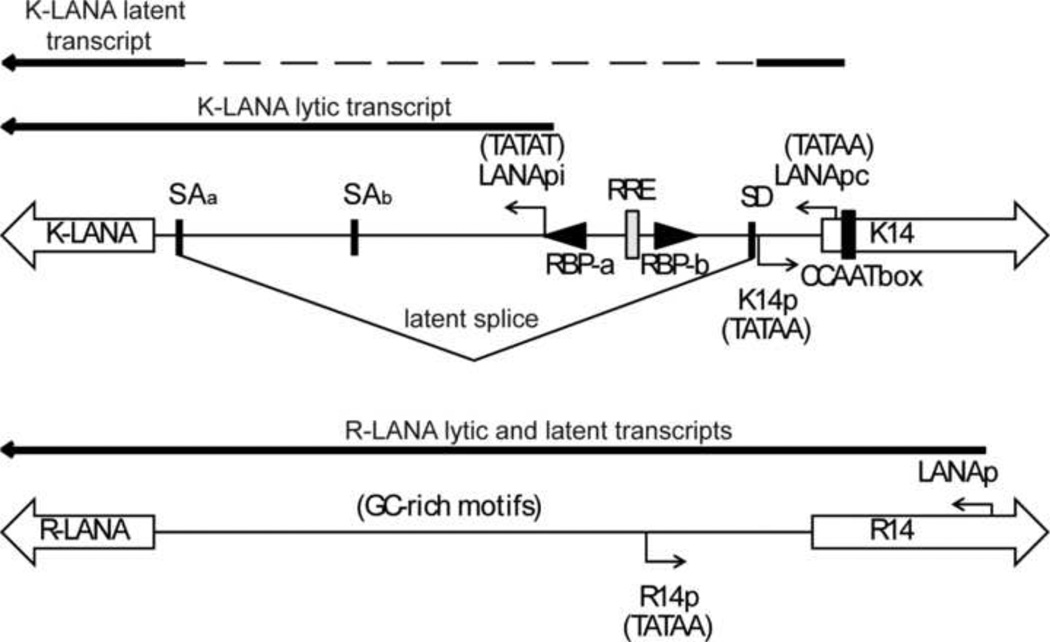
Figure 11. Comparison of the promoter regions of the LANA homologs of KSHV and RRV.
(A) Schematic of the bi-directional promoter region for the LANA (leftward) and K14 (rightward) homologs in KSHV and RRV. The coding regions for the ORF73 homologs (K-LANA and R-LANA) and 0RF74 homologs (K14 and R14) are indicated as large open arrows. The homologous 0RF74 “TATAA” promoter elements (K14p and R14p) are shown. The latency-associated constitutive LANA promoter (LANApc) of KSHV and the Rta-inducible LANA promoter (LANApi) are shown. Splice acceptor (SAa, SAb) and splice donor (SD) sites utilized to produce the latent spliced LANA transcripts are indicated (18, 58, 65). RBP-Jkappa and RRE binding sites in LANApi are shown. RNA transcript and sequence analysis of the RRV LANA gene revealed no evidence for an inducible promoter analogous to the Rta-inducible KSHV LANApi promoter.