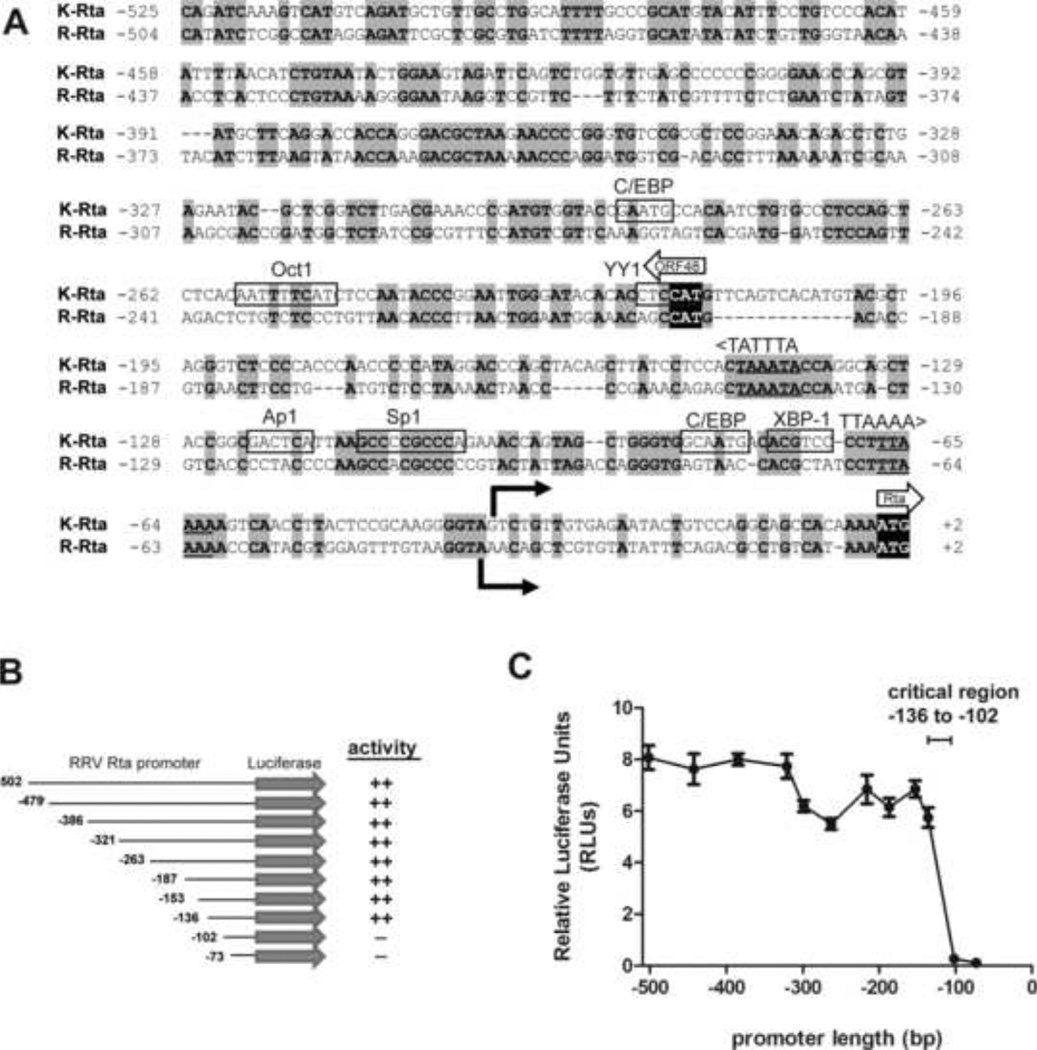
Figure 6. Deletion analysis of the RRV Rta promoter reveals a critical regulatory region.
(A) Comparison of the promoter regions of K-Rta and R-Rta, the replication and transactivator genes for KSHV and RRV, respectively. Nucleotides 71170 to 71697 of KSHV (NC_009333.1) and 66858 to 67364 of RRV (NC_003401.1) genomic sequence were aligned. Nucleotide numbering indicates the position relative to the Rta translational start site. Identical nucleotides are highlighted in gray. Known transcription factor binding sites for C/EBP, Octl, YY1, Apl, Spl, and XBP-1 in the KSHV Rta promoter (9, 39, 56, 67, 68, 70, 74, 75) are indicated. Of these sites, only the Sp1 binding site was conserved in the RRV Rta promoter. Transcriptional start sites for KSHV Rta and RRV Rta (16, 42) are identified by solid arrows. Translational start sites for Rta and ORF48 are shown with block arrows with initiation codons shown in black. TATA-like elements upstream of ORF48 and Rta are shown. (B) 5’ serial truncations of the RRV Rta promoter region were constructed in the pGL2 firefly luciferase backbone. (C) Luciferase activity was measured in extracts from permissive Vero cells transfected with pGL2 R-Rta promoter deletion clones and normalized using pRL-CMV. Error bars represent the standard deviation of results from triplicate wells. The region from −136 to −102 containing the conserved Sp1 binding site was critical for Rta promoter activity.