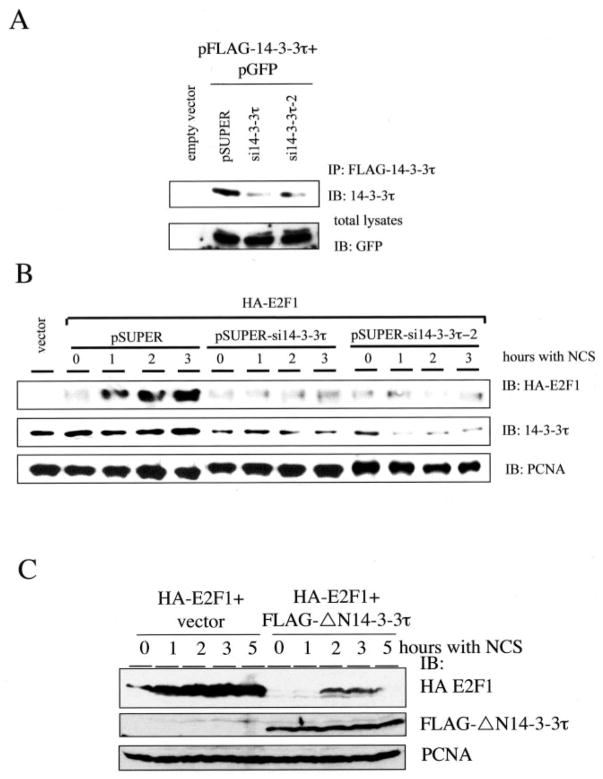
Fig. 3. 14-3-3τ is required for the induction of E2F1 protein accumulation upon DNA damage.
A, HEK293 cells were transfected with pFLAG-14-3-3τ, pGFP and pSUPER or pSUPER vectors expressing two different 14-3-3τ siR-NAs. Transfected 14-3-3τ was immunoprecipitated (IP) with FLAG-beads and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-14-3-3τ antibody. The expression of GFP protein in each transfectant serves as a control. B, knockdown of 14-3-3τ blocks the induction of E2F1 in response to NCS treatment. HEK293 cells, transiently transfected with 14-3-3τ siRNA and HA-E2F1, were treated with NCS (300 ng/ml) for 0, 1, 2, and 3 h. Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies as indicated. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunoblotting was performed to ensure equal protein loading. C, a dominant negative mutant ΔN14-3-3τ inhibited the induction of E2F1 by NCS. HEK293 cells were transfected with HA-E2F1 alone or with pFLAG-ΔN14-3-3τ and treated with NCS. Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies as indicated.