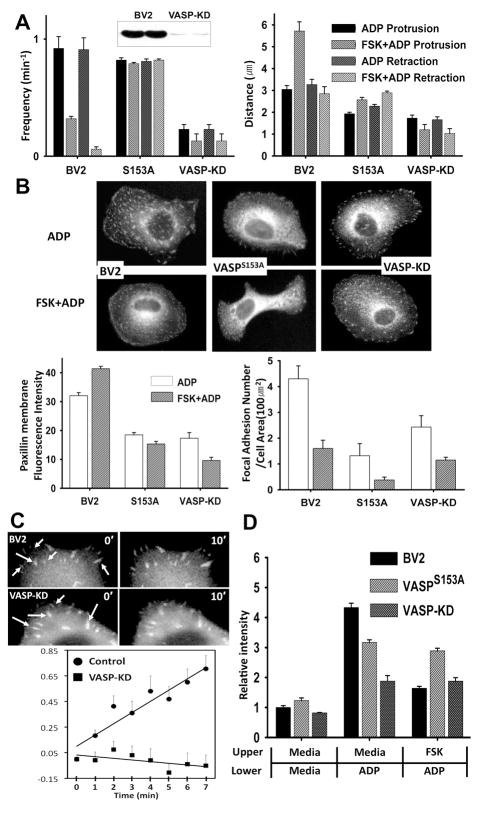
Figure 5.
(A) Membrane ruffle formation in VASP knock-down (VASP-KD) or cells expressing non-phophorylatable VASP mutant (VASPS153A–GFP). Inset shows the reduction of VASP in VASP-KD cells detected by western blot analysis. (B) Changes in the number of focal complexes or adhesions examined by paxillin immunostaining in VASP-KD cells and cells expressing VASPS153A-GFP. (C) Time series of GFP-paxillin-marked adhesion assembly of VASP-KD cells were acquired at 1 min intervals for 20 min and images at 0 min and 10 min are shown. Arrows indicate adhesions. Fluorescence intensities of adhesions at each time point were measured. Points represent average + SEM of the natural log of the ratio of the integrated fluorescent intensity at each time point to the initial fluorescent intensity. Measurements were performed on 10 to 15 individual adhesions from 5–7 cells. (D) Chemotaxis of VASP-KD cells or cells expressing VASPS153A–GFP. Transwell chamber membranes were coated with 3 μg/ml fibronectin for 1 hr and cells were plated. Cells were then assayed for migration toward 100 μM ADP in the continued presence of FSK or OA.