Figure 7. Proposed model describing the role of the cyclic phosphorylation of Sec5 in an engagement-disengagement cycle between the exocyst and its upstream G protein.
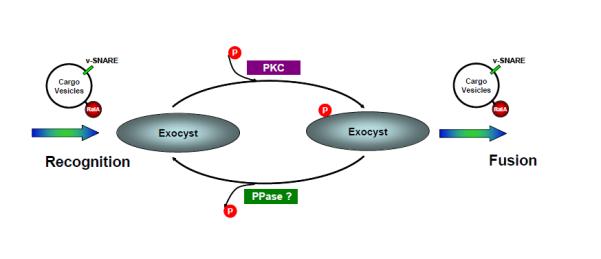
After its activation, the vesicular GTPase RalA interacts with the exocyst protein Sec5, in the process catalyzing the engagement between cargo vesicles and the exocyst. Sec5 subsequently undergoes PKC-dependent phosphorylation within the Ral-binding domain. This phosphorylation allosterically reduces the affinity of its interaction with RalA, resulting in the release of the vesicle from the exocyst so that it can fuse with the plasma membrane. Sec5 then undergoes dephosphorylation by a resident phosphatase, recycling the exocyst for the next round of vesicle recognition.
