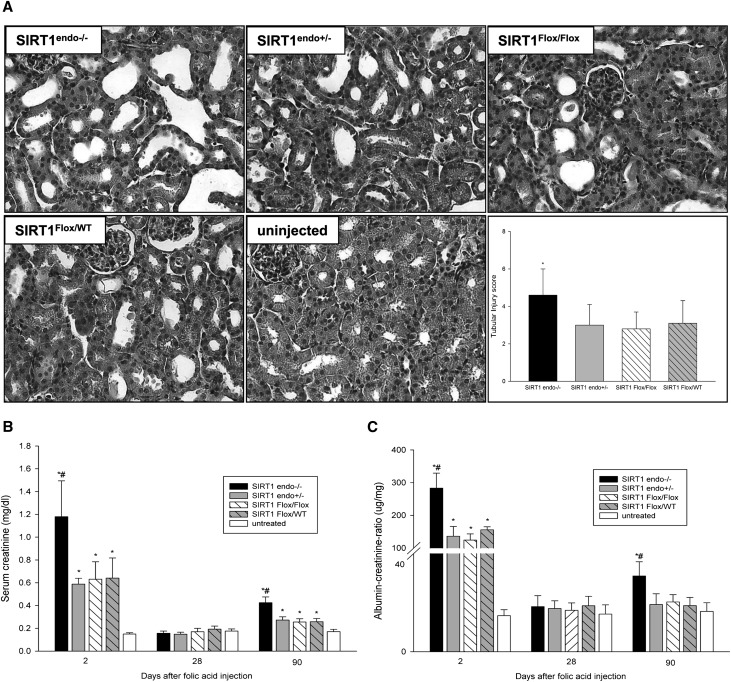
Figure 2.
Acute and chronic effects of nephrotoxic injury. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin–stained kidney sections from 12-week-old SIRT1endo−/− knockout mice, SIRT1endo+/− heterozygote mice, and control mice treated with folic acid. Histomorphologic examination reveals more severe AKI (day 2) in SIRT1endo−/− compared with the other treated groups. Increased serum creatinine levels (B) and higher urinary albumin excretion (C) confirm a much more robust acute response (day 2) in SIRT1endo−/− knockout mice after folic acid injection than in SIRT1endo+/− heterozygote and control mice. Although both parameters have normalized at 28 days after injection of folic acid, SIRT1endo−/− animals show significantly increased serum creatinine levels and albuminuria compared with the other treated groups at 90 days after treatment. The animals in the treatment groups are injected with 250 mg/kg folic acid in 0.3 M NaHCO3 vehicle and euthanized after 2 days (AKI) or 28 or 90 days (chronic fibrotic phase). Untreated mice are injected with vehicle only. There are no significant differences in serum creatinine levels or albuminuria between the untreated groups; therefore, they are presented together as one single group of untreated animals. n=6–7 per group. Data are the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 treated versus untreated animals; #P<0.05 SIRT1endo−/− versus other treated groups at the same time point. Original magnification, ×400.