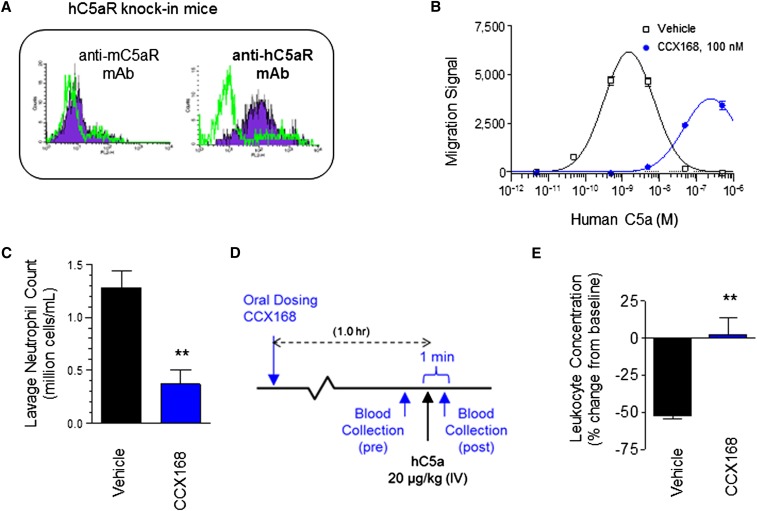
Figure 3.
Leukocytes in mice with human C5aR knock-in and mouse C5aR knock-out express human C5aR and respond to human C5a, and CCX168 inhibits activation via human C5aR. (A) Mouse and human C5aR expression in isolated leukocytes from hC5aR knock-in mice. Flow cytometric leukocyte staining with antibodies specific for mouse or human C5aR is shown in blue with isotype controls (green line) shown for comparison. (B) Chemotaxis of hC5aR knock-in cells in response to a dose range of human C5a in the absence (square) or presence (circle) of CCX168 (100 nM) showing inhibition of chemotaxis by CCX168. Migration signal is a measure of cell numbers migrating between ChemoTX chambers based on intensity of fluorescence of a DNA-binding fluorescent marker. (C) Effects of oral pretreatment with vehicle or a single dose of CCX168 on cell count in the peritoneal lavage 24 hours after intraperitoneal thioglycollate injection. (D) Schematic of the C5a-induced leukopenia study in hC5aR knock-in mice. One hour after oral administration of CCX168, blood was drawn 1 minute before and 1 minute after intravenous (IV) administration of C5a (20 μg/kg); leukocyte concentrations were determined in these blood samples. (E) Following the study outline shown in panel D (n=4 mice/group), CCX168 inhibited the transient depletion of blood leukocytes caused by intravenous administration of C5a. Percentage change from baseline is shown (0, no change; 100, no leukocytes in blood). CCX168 was administered as an oral 30 mg/kg dose in these studies. **P<0.01 t test.