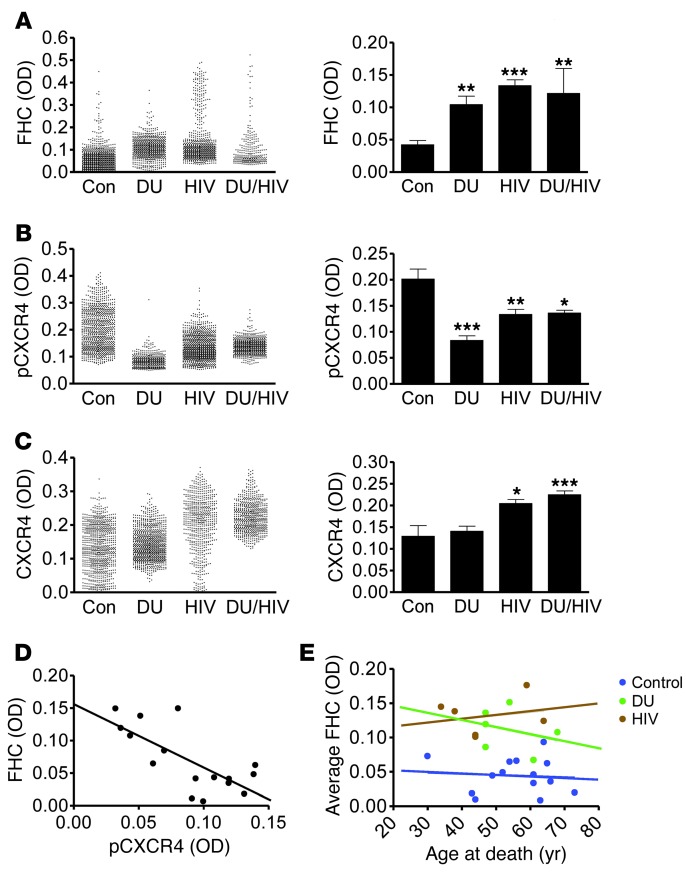
Figure 1. HIV infection and opiate drug use associate with increased FHC and decreased pCXCR4 within neurons of the prefrontal cortex in human HIV-infected and drug-using patients.
OD of FHC (A), pCXCR4 (active) (B), and total CXCR4 (C) within MAP2+ neurons was quantified among control (n = 7–14), drug-using only (DU; n = 5–7), HIV only (HIV; n = 5–16), and drug-using HIV (DU/HIV; n = 3–8) patients. Approximately 100 neurons were analyzed for each patient. Mean OD for each neuron and average neuronal OD for each patient group are shown. (D) Plotting each patient’s average FHC OD to that of pCXCR4 revealed a significant inverse correlation, indicative of a negative relationship between FHC expression and CXCR4 activation (n = 16; Pearson r = –0.724; P = 0.002). (E) No significant relationship was found between average neuronal FHC OD and age at death for any patient group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.