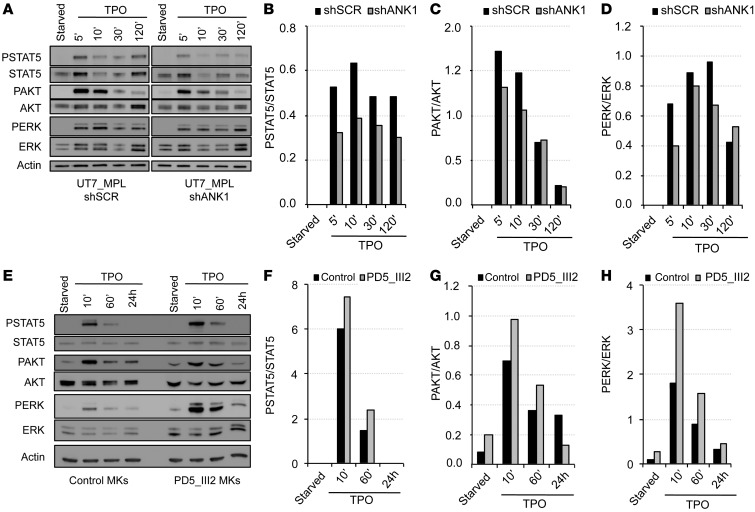
Figure 5. Deregulation of ANKRD26 expression affects TPO/MPL signaling.
(A–D) ANKRD26 inhibition leads to the decreased STAT, AKT, and ERK signaling mediated by TPO in UT7-MPL cells. (A) Western blot analysis of ERK, phospho-ERK (PERK), AKT, phospho-AKT (PAKT), STAT5, phospho-STAT5 (PSTAT5), and actin expression in UT7-MPL cells. Cells were transduced by lentivirus encoding for shANKRD26 (shANK1) or for control (scramble) shRNA (shSCR). Two days later, cells were starved overnight (5% FBS, without cytokines) and stimulated by TPO (20 ng/ml) for 5, 10, 30, and 120 minutes. Experiments were performed 3 times with similar results. (E–H) Maintained ANKRD26 expression in mature MKs of THC2 patient leads to increased TPO-mediated signaling compared with control MKs. (E) Western blot analysis of ERK, PERK, AKT, PAKT, STAT5, PSTAT5, and actin expression in control MKs and in MKs of THC2 patient (PD5_III2). Mature MKs were derived from control or patient blood CD34+ cells in presence of TPO and SCF. At day 8 of culture, they were starved for 24 hours (without cytokines) and stimulated by TPO (50 ng/ml) for 10 minutes, 60 minutes, and 24 hours. (B and F) Histograms representing PSTAT5/STAT5 protein ratio. (C and G) Histograms representing PAKT/AKT protein ratio. (D and H) Histograms representing PERK/ERK protein ratio.