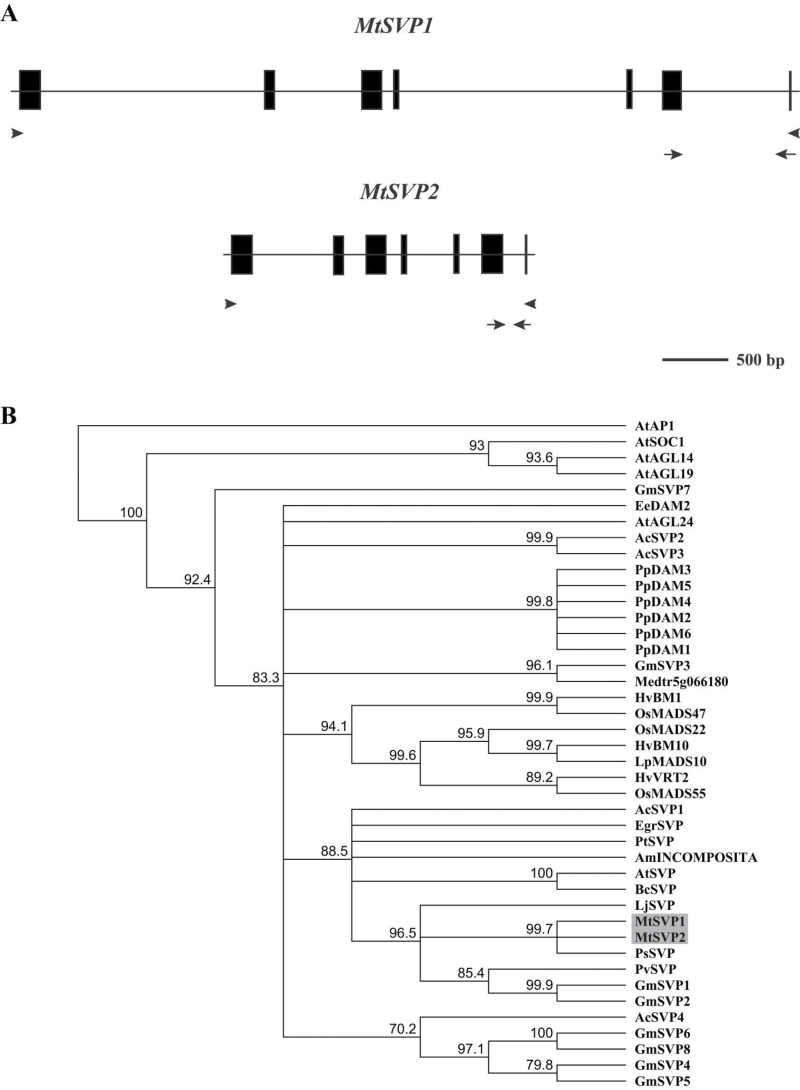
Fig. 1.
Genomic structures of MtSVP1 and MtSVP2 and phylogenetic analysis of SVP-like proteins from different species. (A) The exons are indicated by black boxes and introns by a thin line. The arrows indicate the positions of primers used for quantitative real-time PCR while the arrowheads represent the primers used for cloning the full-length MtSVP1 and MtSVP2 coding sequences from Medicago cDNA. (B) A consensus phylogenetic tree based on the amino acid alignment of MtSVP1 and MtSVP2 predicted proteins (shaded box) and SVP-like proteins from other species. The tree was generated using the Neighbor–Joining (NJ) method via bootstrap resampling with support threshold of 55% and rooted on AtAP1. The numbers indicate the bootstrap values based on 1000 replicates. Ac, Actinidia chinensis; Am, Antirrhinum majus; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Bc, Brassica campestris; Ee, Euphorbia esula; Egr, Eucalyptus grandis; Gm, Glycine max; Hv, Hordeum vulgare; Lj, Lotus japonicas; Lp, Lolium perenne; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Os, Oryza sativa; Pp, Prunus persica; Ps, Pisum sativum; Pt, Poncirus trifoliate; and Pv, Phaseolus vulgaris. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)