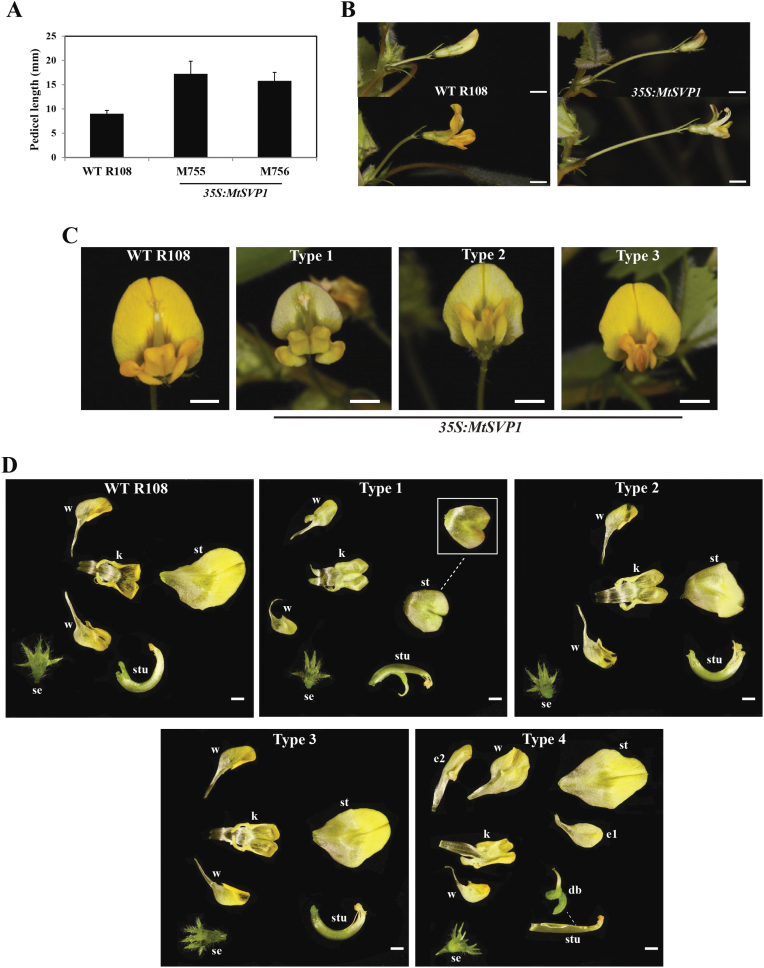
Fig. 6.
Overexpression of MtSVP1 in Medicago results in longer pedicels and smaller and abnormal flowers. (A) Average pedicel length of WT R108 and 35S:MtSVP1 T1 transformants from two lines, M755 and M756. The data are shown as the mean ±SE of 51 flowers from WT R108 (n=5 plants), 54 flowers from M755 (n=5 plants), and 52 flowers from M756 (n=7 plants). The plants were grown in LD after 14 d of cold treatment. The pedicel length was measured from the base of a pedicel to the base of the attached open flower. (B) Photographs showing flowers of WT R108 and transgenic 35S:MtSVP1 plants at the same magnification. (C, D) Flower phenotypes of WT R108 and transgenic Medicago 35S:MtSVP1 T1 plants. Five types of flowers were observed in 35S:MtSVP1 transformants compared with WT R108. Flowers were either similar to WT R108 or had abnormalities (Type 1–Type 4). Type 1 flowers were the smallest flowers observed and were paler in colour compared with WT R108. There was also a purple patch at the back side of standard petal, which appeared to be in a more open form. Type 2 flowers were paler in colour, slightly bigger than Type 1 flowers but still smaller compared with WT R108. Type 3 flowers were the same colour as WT R108, slightly bigger than Type 1 flowers, but still smaller than WT R108. The photos are shown in the same scale. (D) Photographs of floral organs from WT R108 and the different types of flowers from 35S:MtSVP1 transformants as explained above. The inset in Type 1 is the back side of the standard petal showing the purple patch. Another type of flower with extra petals (e1 and e2) and sepal (se) was also seen amongst the 35S:MtSVP1 transformants (Type 4). St, standard petal; w, wing petal; k, keel petal; stu, staminal tube surrounding the carpel; db, developing seed barrel. The photos are shown in the same scale. Bars=2mm in (B), 1.29mm in (C), and 1mm in (D).