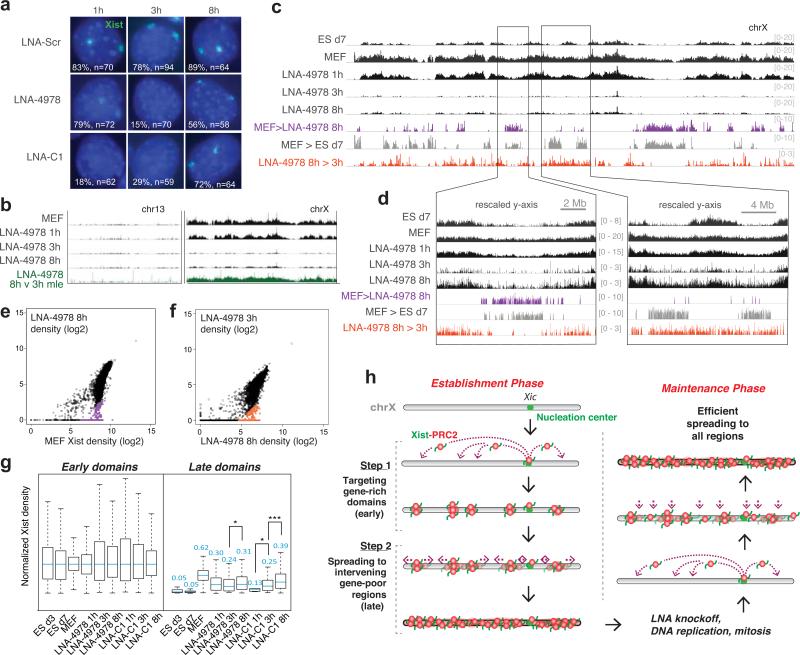
Figure 3. Xist knockoff uncovers a distinct spreading method during the maintenance phase.
a, RNA FISH shows depletion and recovery of Xist RNA (green) in MEF cells after Xist knockoff. %nuclei with Xist clouds and sample size (n) shown. Scr, scrambled LNA. b, Chromosome-wide recovery of Xist after LNA-4978 knockoff on chrX and chr13. Regions of recovery comparing 8h over 3h LNA-4978 were determined using a maximum likelihood enrichment estimate29. c,d, Xist knockoff and recovery across chrX. Colored regions show >10-fold median-normalized differences between samples. (c) Entire chrX (d) zoom of one region with more late domain recovery (right) than the other (left). e,f, Xist CHART signals (40 kb bins) from LNA-4978 8h correlated with MEF (e); LNA-4978 3h correlated against LNA-4978 8h (f). Regions showing >10-fold differences after normalization are colored as shown in panel d. g, Xist recovery in indicated samples, with 40-kb binned Xist densities normalized to median levels of early domains of each sample, to determine how early and late domains recover from knockoff compared to during de novo XCI. Normalized median values for each sample indicated above box. *, p<0.05; ***, p<10−8, Wilcoxon test, as in Extended Data Figs. 7c, 3c. h, Model: distinct methods of Xist spreading during establishment and maintenance.