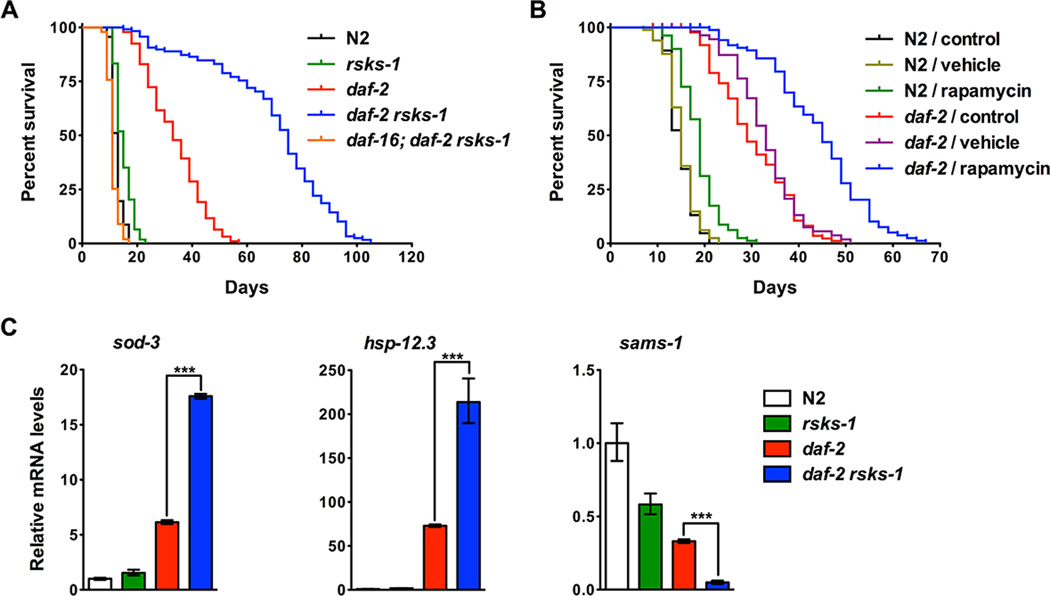
Figure 1. Double mutations in daf-2 and rsks-1 lead to synergistically prolonged longevity that requires DAF-16.
(A) The daf-2 rsks-1 double mutant showed synergistically prolonged longevity (454% extension compared to N2) that is dependent on DAF-16. (B) Inhibition of TOR by rapamycin led to increased lifespan extension in daf-2 compared to N2. Rapamycin (100 μM) extended N2 and daf-2 lifespan by 26% and 45%, respectively (log-rank, p < 0.0001). Animals treated with the vehicle (DMSO) alone did not show significantly affected lifespan (log-rank, p > 0.05). Quantitative data and statistical analyses are included in Table S1. (C) daf-2 rsks-1 animals showed significantly increased DAF-16 transcriptional activity. mRNA levels of DAF-16 targets that are either activated (sod-3 and hsp-12.3) or inhibited (sams-1) by DAF-16 were quantified using qRT-PCR. Asterisks indicate statistical differences using two-tailed t tests: ***, p < 0.001.