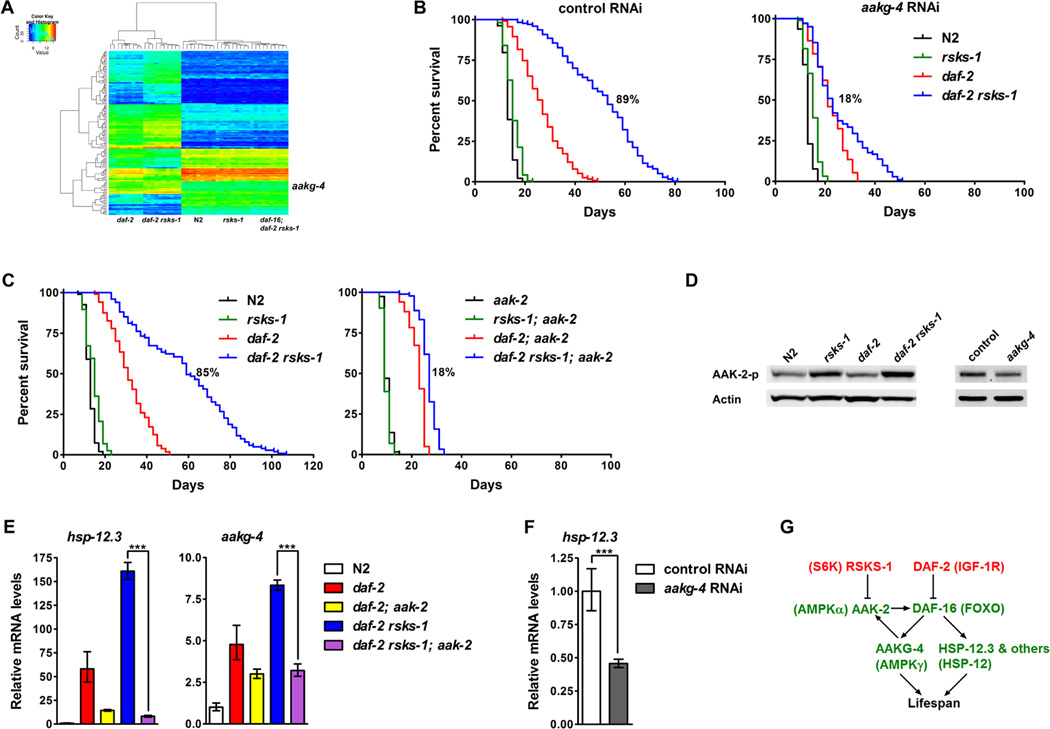
Figure 3. The synergistic longevity by daf-2 rsks-1 is mediated by positive feedback regulation of DAF-16 via AMPK.
(A) Genes that are differentially expressed in daf-2 rsks-1 were identified by microarrays analyses. (B) Identification of aakg-4 as a strong suppressor of daf-2 rsks-1. rsks-1-mediated lifespan extension in daf-2 (daf-2 vs. daf-2 rsks-1): 89% (control RNAi), 18% (aakg-4 RNAi). (C) A deletion in aak-2 suppressed the synergistic longevity by daf-2 rsks-1. rsks-1-mediated lifespan extension in daf-2 (daf-2 vs. daf-2 rsks-1): 85% (with aak-2), 18% (without aak-2). Quantitative data and statistical analyses are included in Table S1. (D) The daf-2 rsks-1 double mutant showed further increased phosphorylation of AAK-2. Inhibition of aakg-4 significantly decreased AAK-2 phosphorylation in daf-2 rsks-1. (E) The aak-2 deletion suppressed the significantly increased DAF-16 transcriptional activity in daf-2 rsks-1. ***, p < 0.001. (F) Inhibition of aakg-4 in daf-2 rsks-1 reduced DAF-16 transcriptional activity. ***, p < 0.001. (G) A model depicting the synergistic lifespan extension through positive feedback regulation of DAF-16 via AMPK.