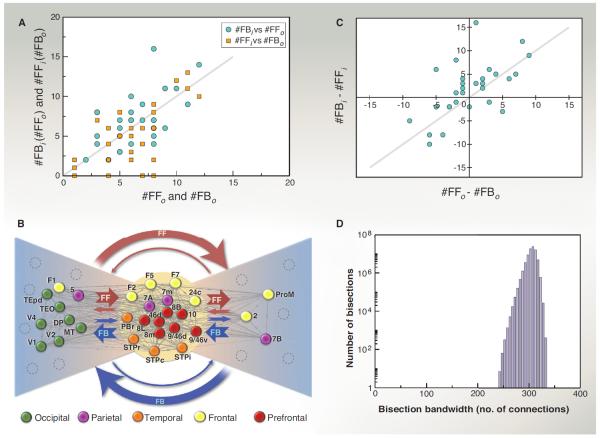
Fig. 4. Bow-tie representation.
Links are classified according to their SLN value being below 0.5 (that is, infra dominated, also called FB) or above 0.5 (that is, supra dominated, also called FF) and according to whether they are oriented toward the core (“out” or “o”) or from the core (“in” or “i”). This generates a total of four possibilities for link types (y is an area from the core, x is noncore): (1) x projecting to y (x→y) as FFo (denoted FFo), (2) x→y as FBo (denoted FBo), (3) y projecting into x (x←y) as FF (or FFi), and (4) x←y as FB (or FBi). (A) The numbers of link types are correlated over the set of all nodes (both from periphery, P, and core, C); the number of FF links into the core (#FFo) correlates on average with the number of FB links from the core (#FBi) and #FFi correlates with #FBo. (B) A bow-tie representation of the G29×29. The dense core (92%) is shown in the middle. The left and right wings of the tie were obtained based on the FF/FB counterstreams into and from the core and their cumulative effective SLN values; see Table 1 legend for details. The cumulative effective SLN is an average SLN to or from the C for the given connection type, weighted by link strengths. In this way, for every area in the P, we obtain four numbers all between 0 and 1, shown in Table 1, columns F to I. A strong FF into C pairs with a strong FB from C, and vice versa, the connections forming FF/FB counterstreams. Computing two indices of effective SLN strengths in absolute value for the two pairs |FFo – 0.5| + |FBi – 0.5| and |FFi – 0.5| + |FBo – 0.5| (columns J and K of Table 1), we classify the nodes into one of two groups (L or R) depending on which value is larger. (C) The imbalance between the number of FF and FB links from a node to C is mirrored on average by imbalance between the FF and FB connections from C to the same node. (D) The edge-complete G29×29 has a very high bisection bandwidth of 242 links, out of 536 total (see Glossary). For electronic data files, see www.core-nets.org.