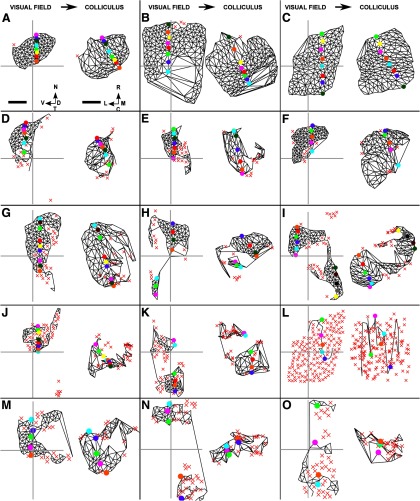
Figure 9.
The largest ordered submaps of the visual field on the superior colliculus for the five HetTKOs, the five HomTKO datasets, and three of the four β2DKO datasets. A, B, HetTKOs where homozygous knock-out of ephrinA2 and ephrinA3 was combined with heterozygous knock-out of ephrinA5. The local and global order in these maps approach that seen in WT maps. C, WT map. D–F, HetTKOs where homozygous knock-out of ephrinA2 and ephrinA5 was combined with heterozygous knock-out of ephrinA3. G–K, HomTKOs involving homozygous knock-out of ephrinA2, ephrinA3, and ephrinA5. I, The nasoventral portion of the visual field projects in the correct orientation, whereas the temporodorsal portion does not. L, The largest ordered submap formed after taking the WT map shown in C and then permuting randomly the set of rostrocaudal coordinate positions assigned to the nodes in the visual field. M–O, Three of the four β2DKO datasets where β2 knock-out was combined with homozygous knock-out of ephrinA2 and ephrinA5. Scale bar: 250 μm (colliculus). Calibration: 20° (visual field). Other conventions as in Figure 2.