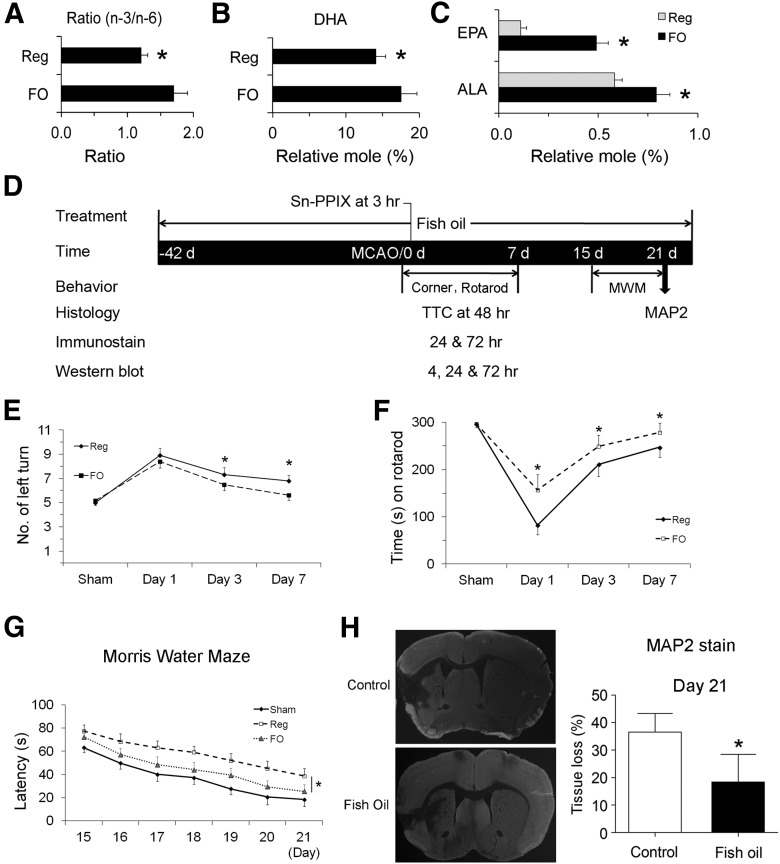
Figure 2.
FO treatment confers long-term neuroprotection against stroke in mice. Mice were fed with either a regular diet or an FO-enriched diet for 6 weeks. Their brains were collected and the lipid profiles of forebrains were analyzed. A–C, The overall n-3/n-6 ratio (A), DHA content (B), and ALA and EPA contents (C) were calculated, showing increased n-3 PUFA contents in the brains (n = 3, *p ≤ 0.05 vs regular diet mice). D, A diagram showing the timeline of FO feeding and the time points for MCAO and various assessments. E, F, The corner test (E) and rotarod test (F) show that FO-fed mice recovered sensorimotor function better than control mice (n = 6–8, *p ≤ 0.05 vs regular diet mice). G, Cognitive function in the Morris water maze during the third week after MCAO is presented as latency to escape the water bath. FO-fed mice recovered better than control mice (n = 5–6, *p ≤ 0.05 vs regular diet-fed mice). H, Representative photographs of MAP2-stained coronal sections and quantitative analyses of tissue loss at day 21 after MCAO (n = 6; data are presented as mean ± SD, *p ≤ 0.05 vs control).