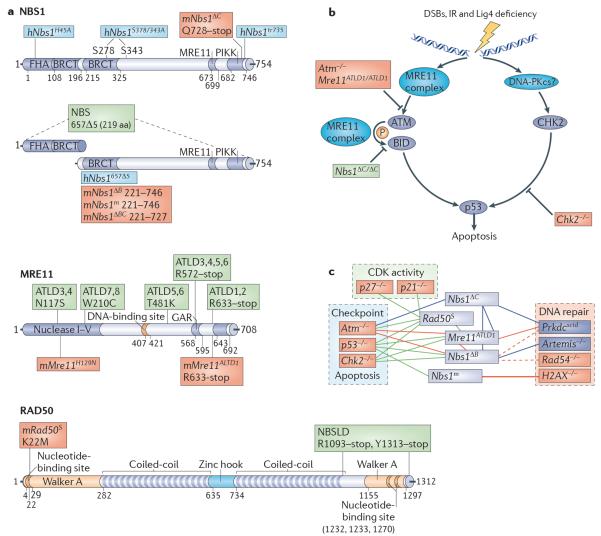
Figure 4. The MRE11 complex in human disease and mouse models.
a | Domain structure of the MRE11 complex. The Nijmegen breakage syndrome 1 (NBS1; also known as nibrin), meiotic recombination 11 (MRE11) and RAD50 components of the human MRE11 complex are illustrated. Domains are indicated by name with the corresponding amino acid numbers shown. Human disease mutations are indicated in green. Mouse alleles are indicated in red and `humanized' mouse alleles in blue. This figure is drawn to scale. b | The MRE11 complex has multiple roles in activating apoptosis after double-strand break (DSB) exposure. The complex activates ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and facilitates the phosphorylation of select ATM substrates, including CHK2 and BH3-interacting domain death agonist (BID), to promote p53-dependent apoptosis through the carboxyl terminus of NBS1. CHK2 signals in parallel, and is possibly activated by the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs). Mouse alleles affecting various steps in the signalling pathway are indicated. Alleles in red impair apoptosis in both the haematopoietic and nervous system and alleles in green affect the haematopoietic but not the nervous system. c | Genetic interactions between mouse MRE11 complex alleles. MRE11 complex alleles used for genetic analyses are shown in green, components of the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ; also known as classical (C)-NHEJ) machinery are shown in blue and other DNA damage or cell-cycle regulators are shown in red. Connecting lines indicate that genetic crosses have been analysed. Blue lines indicate that no synthetic interactions were identified, green lines indicate that synthetic interactions were identified, and red lines indicate synthetic lethality. Dashed lines indicate incomplete penetrance of synthetic lethality. Interacting alleles are classified by their major functions of the DNA damage response, although they may affect other aspects of the response. ATLD, ataxia-telangiectasia-like disease; BRCT, BRCA1 C-terminal; FHA, Forkhead-associated; h, humanized; m, mouse; NBSLD, NBS-like disorder; PIKK, PI3K-related protein kinase.