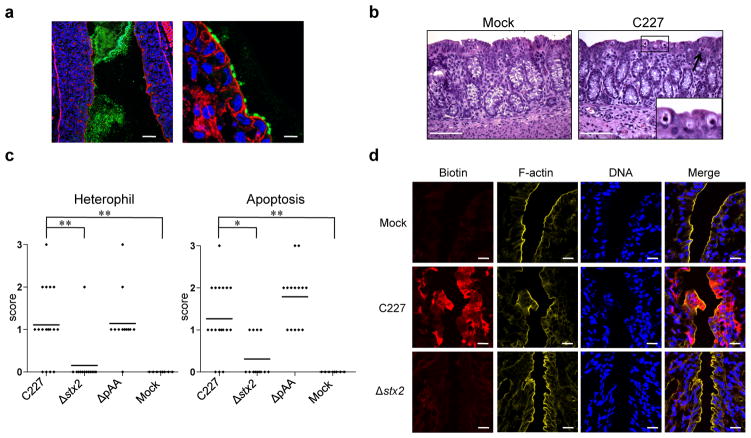
Figure 3. Histopathology in infant rabbits inoculated with E. coli C227 or isogenic mutants.
(a) Representative confocal micrographs showing C227 in the intestinal lumen and attached to intestinal tissue at day 3 PI in the distal colon. C227 was stained with polyclonal antisera against C227 (green) and counterstained with phalloidin-Alexa 568 (red) and DAPI (blue) to detect F-actin and nuclei, respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm (left panel) and 10 μm (right panel). (b) Representative H&E-stained colonic sections from C227 and mock-infected rabbits 3 days PI showing infiltration of heterophils (arrow) and apoptosis (enlarged box). Scale bar=100 μm. (c) Pathology scores for infiltration of heterophils and apoptosis in the distal colon of rabbits inoculated with the indicated strain. Data points represent individual rabbits from 2 and 3 days PI (C227, n=19; Δstx2, n=13; ΔpAA, n=14; Mock, n=8). Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal-Wallis statistic with Dunn’s post-test for multiple comparisons. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. (d) Colonic tissue from rabbits infected with the indicated strain stained with biotin (red) prior to sectioning, then counterstained with DAPI (blue) and phalloidin-Alexa 633 (yellow). Scale bar=20 μm.