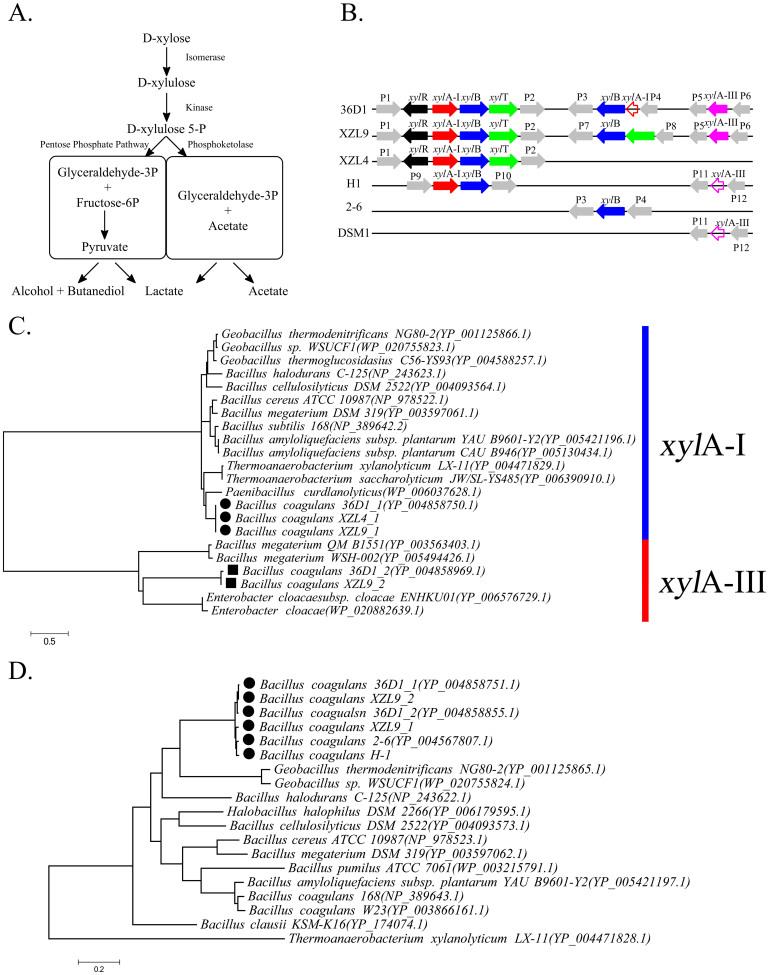
Figure 3. Comparative analysis of xylose metabolism in the B. coagulans strains.
(A) The metabolic pathway for xylose fermentation in lactic acid bacteria. (B) Schematic gene maps of the xylose-utilization genes found in the B. coagulans strains examined in this study. Genes, that were not filled, are pseudogenes. xylR: DNA-binding transcriptional activator; xylAI: xylose isomerase Type I; xylB: xylulokinase; xylT: Xylose H+-symporter; xylAIII: xylose isomerase Type III; P1: quinolinate synthetase; P2: iron-containing alcohol dehydrogenase; P3: peptidase; P4: hypothetical protein; P5: PfkB domain-containing protein; P6: LacI family transcriptional regulator; P7: beta-ketoacyl reductase; P8: hypothetical protein; P9: breakpoint of contigs; P10: hypothetical protein; P11: hypothetical protein; P12: 6-phospho-3-hexuloisomerase; (C) Maximum likelihood tree of xylA genes. The genes marked by filled circles ( ) are from B. coagulans strains and are homologs of xylA in B. subtilis. The genes marked with squares (
) are from B. coagulans strains and are homologs of xylA in B. subtilis. The genes marked with squares ( ) are from B. coagulans strains, and are the novel xylose isomerases discovered in this study. (D) Maximum likelihood tree of xylB genes. The genes marked with filled circle (
) are from B. coagulans strains, and are the novel xylose isomerases discovered in this study. (D) Maximum likelihood tree of xylB genes. The genes marked with filled circle ( ) are from B. coagulans strains. The accession numbers of these genes downloaded from the NCBI database are shown in the parentheses. A scale bar for the genetic distance is shown at the bottom.
) are from B. coagulans strains. The accession numbers of these genes downloaded from the NCBI database are shown in the parentheses. A scale bar for the genetic distance is shown at the bottom.