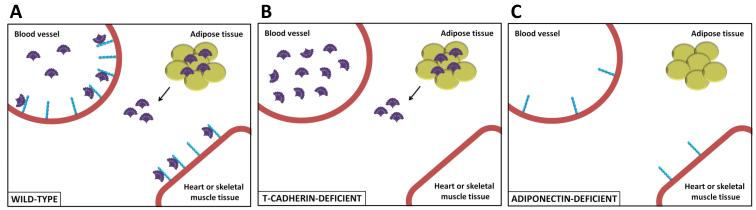
Figure 1. T-cadherin is essential for localization of adiponectin to cardiovascular tissues.
A) In wild-type mice, high molecular weight adiponectin (shown in purple) is tethered to vascular and muscle tissue through binding T-cadherin (shown in blue). B) In the absence of T-cadherin, adiponectin is liberated leading to increased serum adiponectin levels while the adipokine is absent from cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue. C) In the setting of adiponectin-deficiency, T-cadherin tissue expression is reduced suggesting a feedback regulatory axis between these proteins.