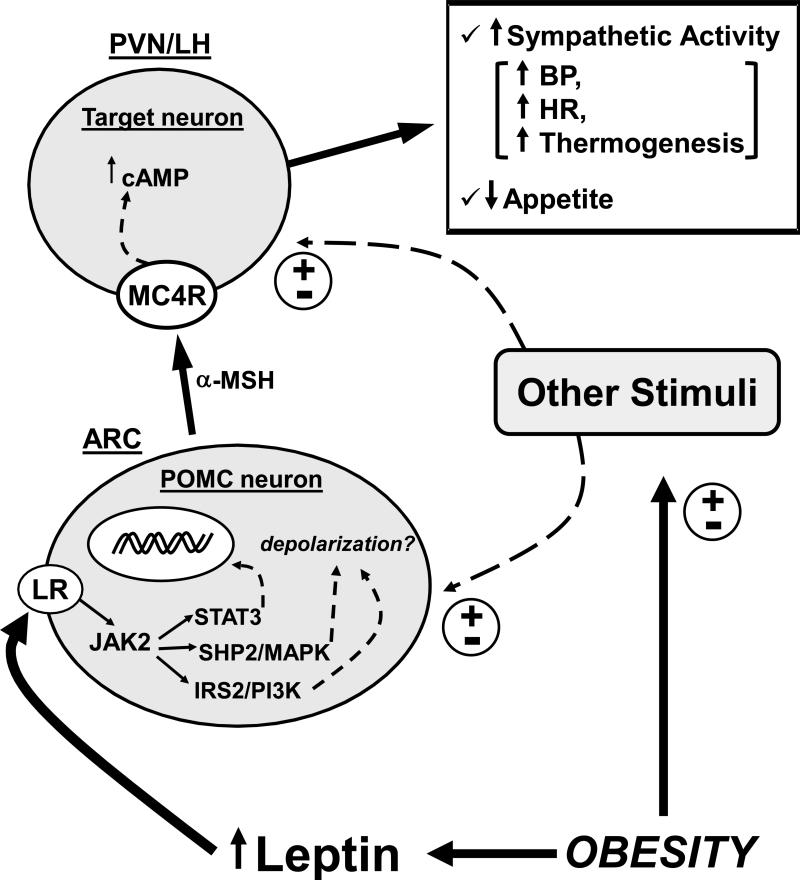
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the interaction between obesity, leptin and the brain melanocortin system. LR indicates leptin receptor; MC4R indicates melanocortin 4 receptor; POMC indicates proopiomelanocortin protein; α-MSH indicates α-melanocyte stimulating hormone; cAMP indicates cyclic adenosine monophosphate; BP indicates blood pressure; HR indicates heart rate; PVN indicates paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus; LH indicates lateral hypothalamus; ARC indicates arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus; (±) indicates stimulation or attenuation. Note: although this schematic representation highlights the importance of POMC neurons locates in the ARC and projecting to MC4R containing neurons in the PVN and lateral hypothalamic area, MC4R are expressed in many other important nuclei in the hypothalamus and other forebrain regions as well as in the brainstem where POMC neurons have also been found. The role of brainstem POMC neurons as well as of MC4R containing neurons in this region in regulating appetite and cardiovascular function, however, are still unclear.