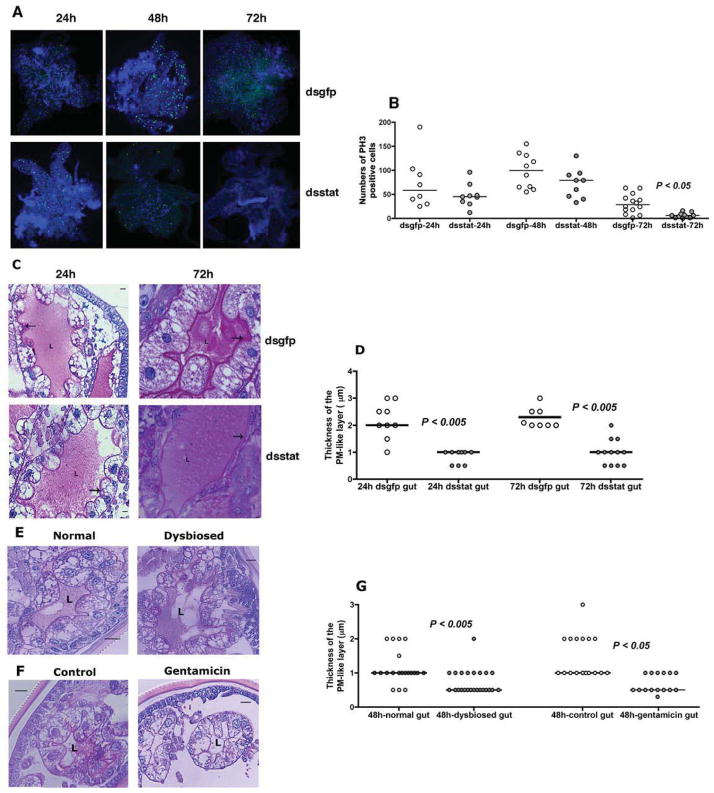
Figure 3. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of stat expression correlates with altered gut barrier integrity.
A. Immunofluorescence microscopy to assess mitotic activity in nymhpal guts of dsgfp or dsstat RNA-injected nymphs at 24, 48, and 72 h of feeding as seen by PH3 positive signal (green/Alexa 488). Nuclei stained with DAPI (Blue). Magnification x10; and B. Quantitation of PH3 positive signal/gut. Each data point represents one gut. C. Periodic acid-Schiff’s (PAS) stain of Carnoy’s fixed and sectioned 24 and 72h fed guts of dsgfp or dsstat RNA-injected nymphal guts; and D. Thickness of the PM-like layer. PAS stain of Carnoy’s fixed and sectioned 48 h fed guts of: E. Normal and dysbiosed larvae; and F. PBS or gentamicin-exposed larvae stained with PAS; and G. Thickness of the PM-like layer. ‘L’ indicates the lumen and arrow indicates the PM layer. In C, E and F, scale bars are 10 μm and magnification at 40x. In D and G, each data point represents an arithmetic average of 3 measurements/field/gut. Horizontal bars represent the median and mean values significantly different in a non-parametric two-tailed Mann-Whitney test (P < 0.05) indicated. See also Fig S2.