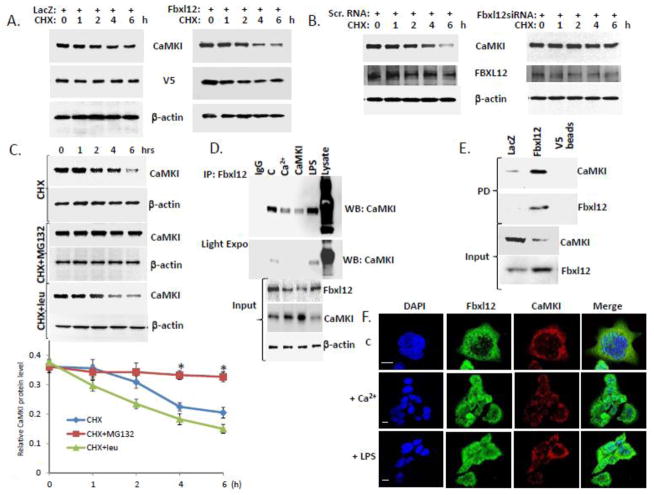
Figure 2. Fbxl12 binds CaMKI to trigger its degradation.
(A–B) CaMKI half-life was determined after Fbxl12 plasmid overexpression (A) or knockdown using scramble (scr) RNA or Fbxl12 siRNA and cycloheximide (CHX) (B). (C) Levels of CaMKI in MLE cells exposed to MG132 and leupeptin in combination with cyclohexamide. Bottom graph shows quantification of CaMKI levels. (D) Immunoprecipitation using Fbxl12 antibody from MLE lysates after cells were exposed to Ca2+ or LPS or cells transfected with CaMKI plasmid; (C=control). Immunoprecipitants were analyzed by immunoblotting using CaMKI antibody. (E) MLE cells were transfected with V5-LacZ or V5-Fbxl12 plasmids followed by pull down (PD) assays using V5 agarose beads and immunoblotting with CaMKI and Fbxl12 antibodies. (F) Cells exposed to Ca2+or LPS were immunostained for Fbxl12 and CaMKI to determine subcellular localization. The data from each panel represents n=3 separate experiments. *P < .01 versus CHX treatment. Scale bar, 10 μm.