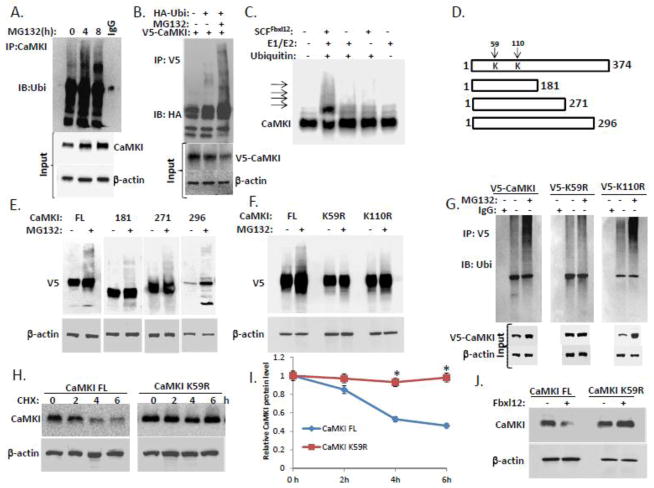
Figure 3. Fbxl12 targets CaMKI for ubiquitination.
(A) In vivo ubiquitination assays. Ubiquitinated CaMKI was detected by immunoprecipitation of endogenous CaMKI followed by immunoblotting for ubiquitin after exposing cells to MG132. (B) MLE cells were transfected with V5-tagged CaMKI alone or co-transfected with HA-ubiquitin followed by MG132 exposure. Cells were then lysed and ubiquitinated V5-CaMKI was detected by immunoprecipitation with V5 antibodies followed by immunoblotting for HA antibodies. (C) In vitro ubiquitination assays. Purified SCF complex components were incubated with V5-CaMKI. The arrows show poliubiquitinated CaMKI. (D) Diagram of CaMKI deletion mutants. Arrows indicate putative ubiquitin acceptor sites. (E) Immunoblot analysis of cells transfected with V5-CaMKI FL or truncated V5-tagged CaMKI mutant plasmids followed by exposure to MG132. (F) Immunoblot analysis of cells transfected with V5-CaMKI FL or V5-tagged CaMKI point mutant plasmids (K59R and K110R) followed by exposure to MG132. (G) Cells transfected with V5-tagged (V5-CaMKI FL) or V5-tagged CaMKI point mutant plasmids (V5-K59R and V5-K110R) were exposed to MG132 and then processed for immunoprecipitation using V5 antibodies followed by immunoblotting with anti-ubiquitin antibodies. (H) Determination of CaMKI half-life using cycloheximide in cells expressing either CaMKI FL or the CaMKI K59R mutant plasmids with quantification (I). (J) Levels of CaMKI in the cells co-transfected with CaMKI FL or CaMKI K59R mutant plasmids after ectopic expression of Fbxl12 plasmid (data are from n=3 experiments). *P < .01 versus CHX-treated CaMKI FL.