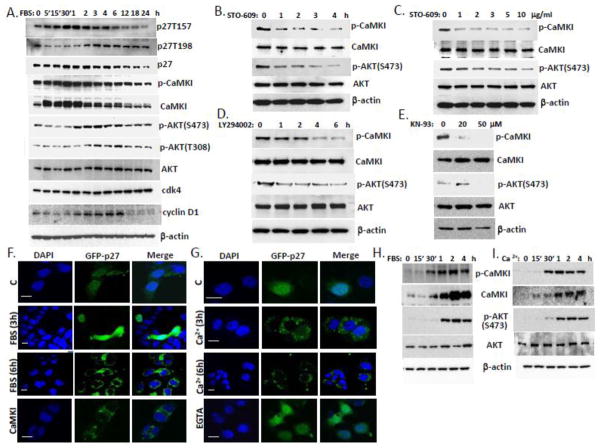
Figure 8. Coordinate regulation of CaMKI and AKT activities via Ca2+ and serum control p27 localization in lung epithelia.
(A) A549 cells were synchronized by serum starvation for 48 h. After 10% FBS addition cells were collected at indicated times and processed for immunoblotting for proteins of interest. (B, C) MLE cells were exposed to the CaMKK inhibitor, STO-609 (10 μg/ml) at various times (B) and concentrations (C, 2 h). (D, E) Cells were also exposed to the AKT inhibitor, LY294002 (30 μM) at various time (D) or CaMKI inhibitor, KN-93 for 1 h (E) and then analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against CaMKI, AKT, and phosphorylation forms. (F,G) MLE cells transfected with GFP-p27 were starved by serum depletion for 48 h and then exposed to 10% FBS (A) or 2 mM Ca2+ (B) followed by fixation at indicated times and immunostaining. Some of these cells were pre-incubated with EGTA as described above or co-transfected with CaMKI plasmid. DAPI was used for visualization of nuclei. Scale bar, 10 μm. (H,I) MLE cells were synchronized by starvation for 48 h and then exposed to 10% FBS (H) or 2 mM Ca2+ (I) for indicated times. Cells were then harvested and analyzed by immunoblotting with CaMKI and AKT antibodies (data are from n=3 experiments).