Figure 3.
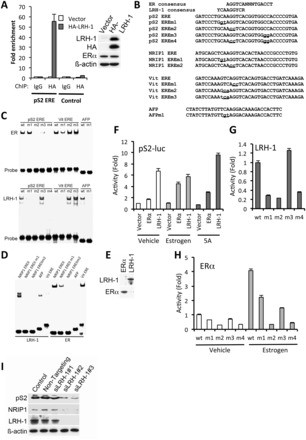
LRH-1 regulates pS2 gene expression through binding to the pS2 ERE. (A) ChIP was carried out using IgG (control) or HA antibodies, following transfection of MCF-7 cells with empty vector or HA-LRH-1, followed by real-time PCR using primers for the pS2 ERE region, or with primers amplifying a region upstream of the pS2 ERE (control), as described (14). For each PCR, enrichment is shown relative to the vector control, as mean values for three replicates; error bars represent SEM. Western blotting of HA-LRH-1–transfected MCF-7 cell extracts is also shown. (B) Sequences for consensus ERα and LRH-1 binding sites are shown above the sequence of the pS2 ERE. The NRIP1 intronic ERE, chicken vitellogenin ERE and the LRH-1 binding sites in the mouse AFP gene. Mutations generated in these sequences are shown in lower case and are underlined. (C–E) EMSA was carried out using oligonucleotides having the sequences shown in (B). LRH-1 and ERα were produced using coupled in vitro transcription/translation (IVTT). Western blotting of IVTT products for LRH-1 and ERα is shown in (E). (F) COS-1 cells were transfected with pS2-luc, together with ERα and LRH-1, as shown. Reporter gene activities were corrected for transfection efficiency by normalizing to Renilla luciferase activity and are shown relative to reporter gene activity for the vehicle-treated vector control. Shown are the mean pS2-luc activities from three independent transfections; errors bars = SEM. (G and H) COS-1 cells were transfected with LRH-1 (G) or ERα (H), together with pS2-luc or mutant reporters, as shown. Following normalization for the transfection control (renilla), activities are shown relative to the activities obtained for pS2-luc.
