Figure 2.
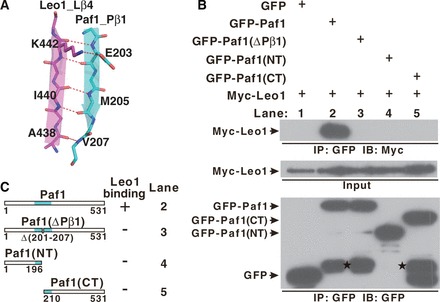
The interaction between Paf1 and Leo1. (A) The interface details in the Paf1(161–250)-Leo1(370–462) heterodimer. The β1 strand of Paf1 (Pβ1) is colored in cyan, and the β4 strand of Leo1 (Lβ4) is colored in magenta. Hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds are shown as dotted red lines. (B) Co-IP experiments of the interaction between Leo1 and various Paf1 constructs. Extracts were prepared from HEK293T cells transfected with various combinations of plasmids as indicated, immunoprecipitated with agarose-conjugated anti-GFP and subsequently immunoblotted with anti-Myc (top panel) or anti-GFP (bottom panel) as indicated. The top panel shows the immunoprecipitation (IP) results. The middle panel represents 2% of the input material Myc-Leo1 for each IP. The bottom panel represents the IP of GFP and various GFP fusion proteins (GFP-Paf1, GFP-Paf1(ΔPβ1), GFP-Paf1(NT), GFP-Paf1(CT)). Bands indicating degradation products in GFP-Paf1, GFP-Paf1(ΔPβ1) and GFP-Paf1(CT) are marked by stars. (C) Summary of results obtained in (B). ‘+’ or ‘−’ indicates binding or no binding, respectively, between Leo1 and Paf1 in the co-IP experiments. A schematic representation of the full length and mutated Paf1 constructs used in the IP experiments is shown.
