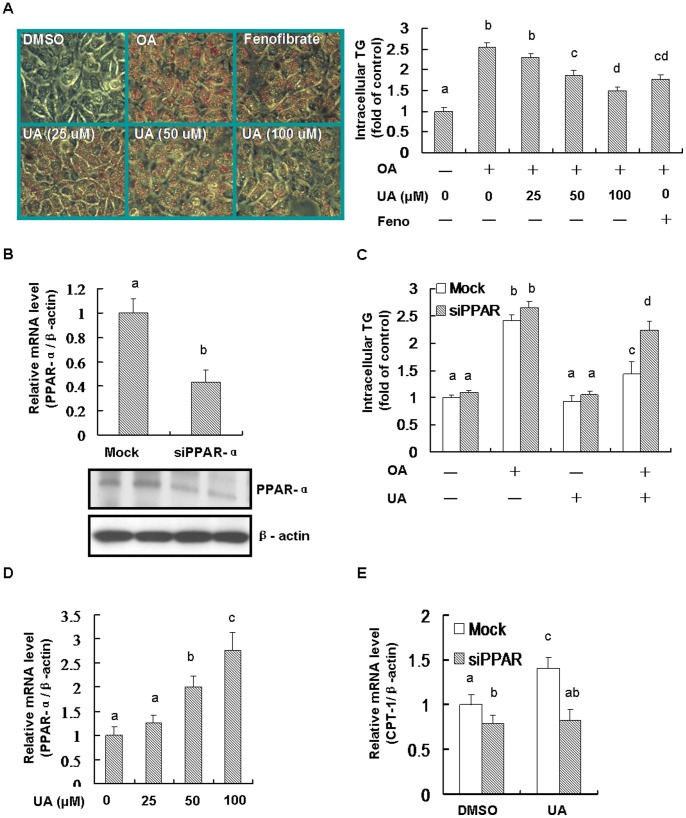
Figure 6. PPAR-α contributed to the anti-steatosis role of UA in HL-7702 cells.
Equal (DMSO) was added into the medium for each group. Cells were seeded into 6-well plate and incubated with oleic acid (OA, 0.5 mM) for 24 h, and then OA was removed and the cells were treated with UA (100 µM, or as indicated) or fenofibrate (Feno, 100 µM) for another 24 h. For PPAR-α knockdown, siRNA was used according to the instructions as described in the Methods. (A) Cell were stained with oil red O and imaged by microscope. The intracellular TG was detected by triglyceride assay kit (Applygen Technologies Inc, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. (B) The levels of mRNA and protein of PPAR-α were detected for testing the siRNA efficiency. (C) Knockdown PPAR-α inhibited the anti-steatosis role of UA and. (D) UA activated PPAR-α mRNA expression. (E) Knockdown PPAR-α blocked UA stimulated increase of CPT-1. Different alphabet indicates statistically significant differences (P<0.05). Data were expressed as means ± SD. All the experiments were repeated at least 3 times.