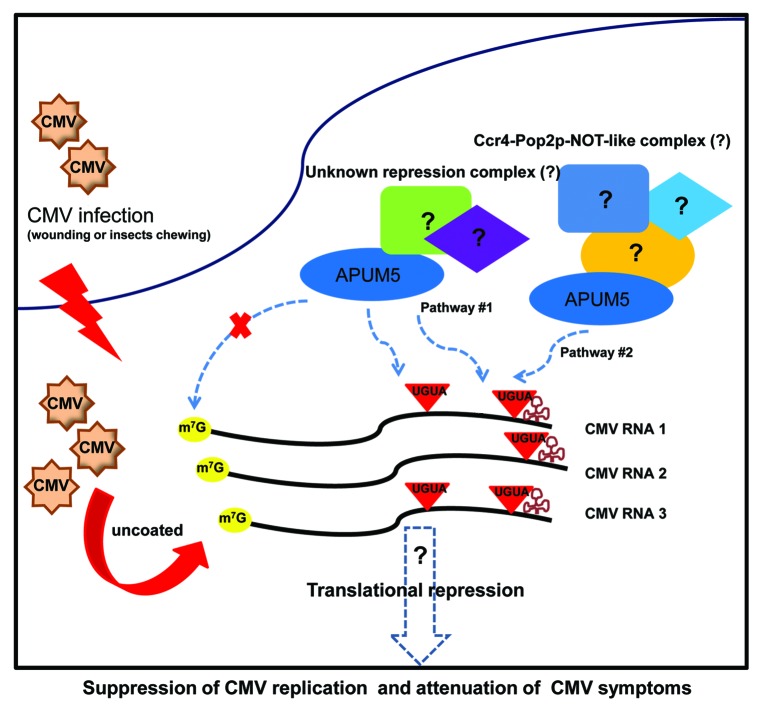
Figure 2. Proposed working model for APUM5 suppression of CMV infection. First, CMV entry into the host cells occurs by mechanical wounding or insects chewing. Then CMV RNAs replicate and synthesize viral proteins. CMV RNAs are stabilized by a tRNA-like structure (TLS) which is recognized by tRNA-specific enzymes. APUM5 recognizes the CMV 3′ UTR and some internal Pumilio binding motifs in the CMV genome either with unknown repression complexes or in association with Ccr4-Pop2p-NOT-like complex. Finally, APUM5 suppresses CMV infection via the direct binding of viral RNAs and attenuates CMV symptoms.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.