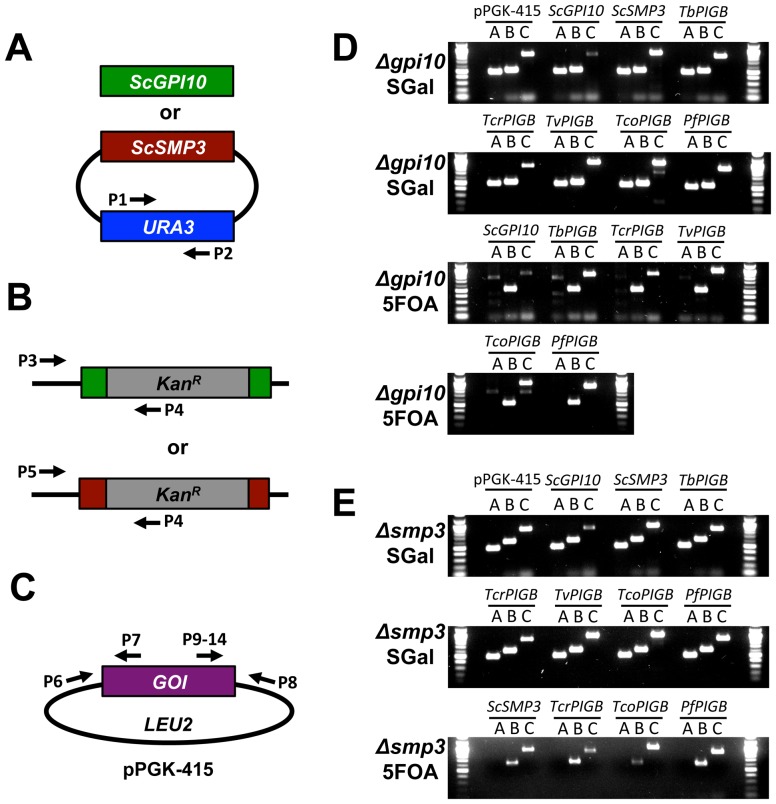
Figure 3. PCR confirmation of yeast strains.
A–C. Schematics of PCR reactions used to confirm strains. See Table S3 for sequences of the indicated primers. A. To confirm the presence (on SGal) or absence (on 5FOA) of the pGAL rescuing plasmid, the URA3 locus within this plasmid was amplified. B. To confirm that the endogenous gpi10 or smp3 locus was indeed null in all strains, forward primers residing in the 5′UTR of the genes were coupled with a reverse primer that sits within the kanamycin cassette that was inserted into the gene locus upon null strain generation. C. To confirm the presence of the pPGK plasmid, PCR was performed using a primer within the pPGK vector, coupled with a primer in the 3′end of the coding region of the PIGB gene of interest. D–E. Results of PCR experiments to confirm all yeast strains shown in Figure 2. DNA was isolated from all strains and the PCRs described in A–C were performed. D. gpi10Δ strains before (SGal) and after (5FOA) plasmid shuffling. E. smp3Δ strains before (SGal) and after (5FOA) plasmid shuffling. Reactions A–C correspond to the schematics A–C at left. Amplicon sizes are: Reaction A: 500 bp; Reaction B: 534 bp for gpi10, 616 bp for smp3; Reaction C: 902 bp for pPGK-415, 891 bp for pPGK-ScGPI10, 922 bp for pPGK-ScSMP3, 800 bp for pPGK-TbPIGB, 820 bp for pPGK-TcrPIGB, 879 bp for pPGK-TvPIGB, 932 bp for pPGK-TcoPIGB and 908 bp for pPGK-PfPIGB.