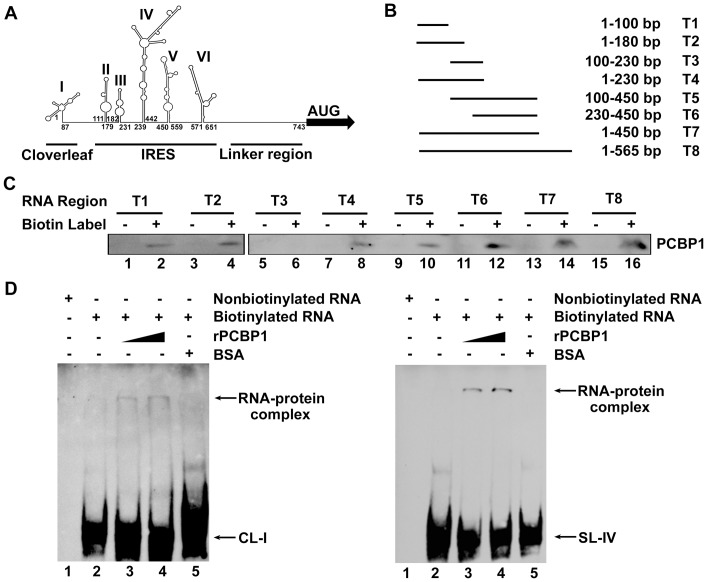
Figure 2. Determination of the sequences in 5′UTR of EV71 RNA required for the binding of PCBP1.
(A) The secondary structure of the full-length 5′UTR of EV71 RNA was predicted using the M-FOLD software (http://mfold.rna.albany.edu). In this predicted secondary structure, six domains (or stem-loops) were shown with first and last nucleotides numbered: domain I (nt 1 to 87), II (nt 111 to 179), III (nt 182 to 231), IV (nt 239 to 442), V (nt 450 to 559), and VI (nt 571 to 651). The three functional regions, cloverleaf, IRES, and linker, were underlined based on previous report [11]. (B) A series of plasmids carrying different deletions in the six stem-loops of EV71 5′UTR were generated: pcDNA3.0-5′UTR (T1, 1–100), (T2, 1–180), (T3, 100–230), (T4, 1–230), (T5, 100–450), (T6, 230–450), (T7, 1–450), and (T8, 1–565). (C) The plasmids were linearized and transcribed into RNA in vitro, which were then labeled with biotin-16-UTP. For the pull-down assay, cell extracts were mixed with these biotinylated EV71 5′UTR RNAs or nonbiotinylated RNAs as control (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15). The complex was dissolved and PCBP1 protein was determined by western blot using a mouse anti-PCBP1 antibody (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16). (D) EMSA assay for domain I (CL-I) and IV (SL-IV). Labeled RNA (CL-1 or SL-IV) (0.5 µg) was incubated with rPCBP1 at 0, 0.1, and 0.2 µg (lanes 2 to 4) or BSA at 0.2 µg (lane 5), respectively. No-labeled RNA was used as a control (lane 1). The RNA-protein complex was separated from free probe RNA and examined by an EMSA. The bound RNA is indicated by an arrow.