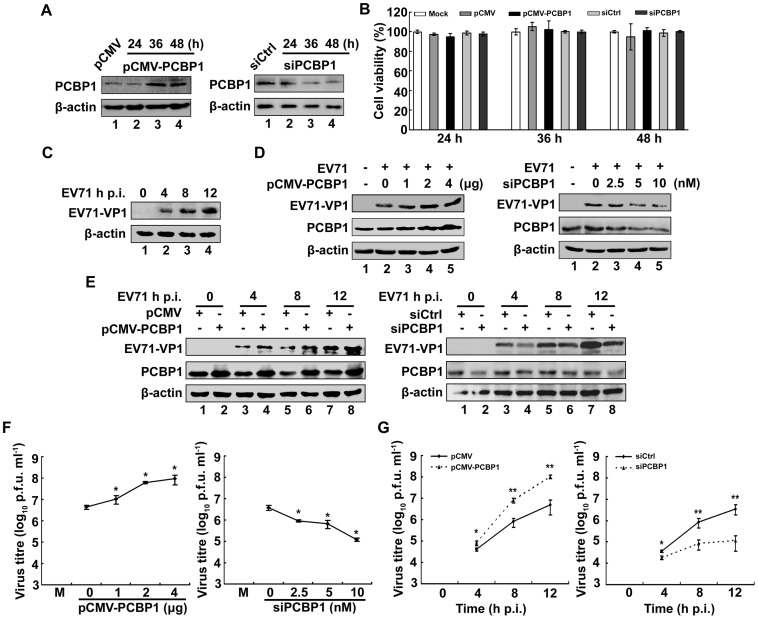
Figure 6. Analysis of PCBP1 in the regulation of EV71 viral protein expression and virus production.
(A) RD cells were transfected with pCMV-PCBP1 (to over-express PCBP1), pCMV (a negative control of pCMV-PCBP1), siPCBP1 (to knock-down PCBP1) and siCtrl (a negative control of siPCBP1), respectively. At 24, 36, and 48 h post-transfection, cells extracts were prepared and proteins were detected by western blot using mouse anti-PCBP1 antibody or mouse anti-β-actin antibody. (B) RD cells were transfected with pCMV-PCBP1, pCMV, siPCBP1, and siCrtl, respectively. At 24, 36, and 48 h post-transfection, viability of transfected cells were determined by MTT assay. The viability of mock cells was normalized to 100%. Data are from three independent experiments with similar results. (C) RD cells were infected with or without EV71 at an MOI of 5 for 4, 8, and 12 h. Mock-infected and EV71-infected cells were lysed and proteins were detected by western blot analysis using antibodies to EV71 VP1 protein or β-actin protein. (D) RD cells were transfected with pCMV-PCBP1 at different concentrations (0, 1, 2, and 4 µg) or with pCMV at different concentrations (4, 3, 2, and 0 µg), siPCBP1 at different concentrations (0, 2.5, 5, 10 nM) or with siCtrl at different concentrations (10, 7.5, 5, 0 nM), respectively, for 36 h, and then infected with or without EV71 at an MOI of 5 for 12 h. Mock-infected and EV71-infected cells were lysed and proteins were detected by western blot analysis using antibodies to EV71 VP1 protein, PCBP1 or β-actin protein. (E) RD cells were transfected with pCMV-PCBP1, pCMV, siPCBP1, and siCtrl, respectively, for 36 h, and then infected with EV71 at an MOI of 5 for 4, 8, and 12 h. EV71-infected cells were lysed and proteins were detected by western blot analysis using antibodies to EV71 VP1 protein, PCBP1 or β-actin protein. (F) Cell culture supernatants from (D) were prepared and subjected to plaque assays and viral infectivity titers of culture supernatants (plaque forming units per ml, PFU/ml) on EV71-infected RD cells were determined. (G) Cell culture supernatants from (E) were collected and viral infectivity titers in supernatants were determined. Viral infectivity titers are expressed as means ± S.E. (n = 3) of three independent experiments (**, p<0.01; *, p<0.05).